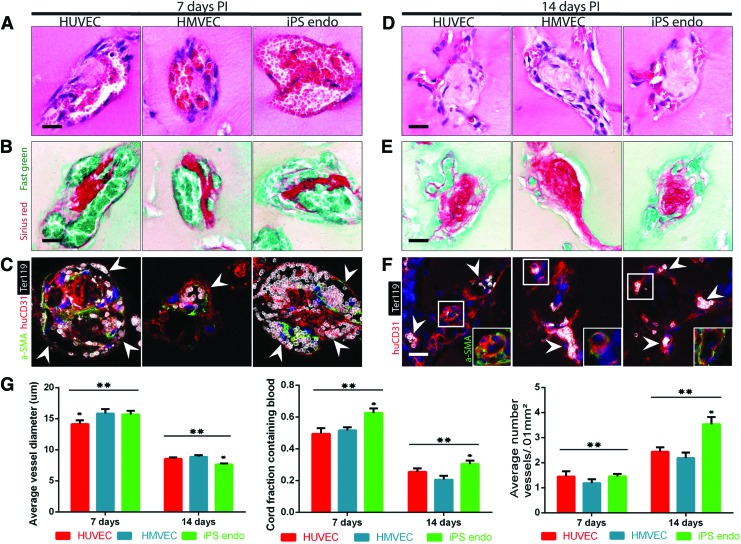
FIG. 4.
Translational cell types. (A) H&E staining of cords composed of HUVECs, human microvascular endothelial cells (HMVECs), and induced pluripotent stem cell-derived ECs (iPS ECs) resected after 7 days and (D) 14 days in vivo suggests the presence of blood in large vessels at 7 days that organize into small capillaries by 14 days (scale bar, 50 μm). (B) Sirius red/Fast green staining of collagen within the cords resected after 7 days and (E) 14 days in vivo. (C) Ter-119 (erythrocytes, white), human-specific CD31 (human ECs, red), and α-SMA (pericytes, green) staining positively identify RBCs and ECs and suggest that vessels consist of implanted human endothelium with perivascular colocalization at 7 days (arrowheads: individual vessels) and (F) 14 days postimplantation (PI) [arrowheads: individual capillaries, box: α-SMA (pericytes, green); scale bar, 50 μm]. (G) Quantification of blood area, vessel diameter, and vessel numbers for translational cell types at different time points. *A p-value of <0.05 for comparison. Error bars SEM, n≥20, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. **A p-value of <0.05 for comparison of each group between time points. Error bars SEM, n≥20, t-test. Color images available online at www.liebertpub.com/tec