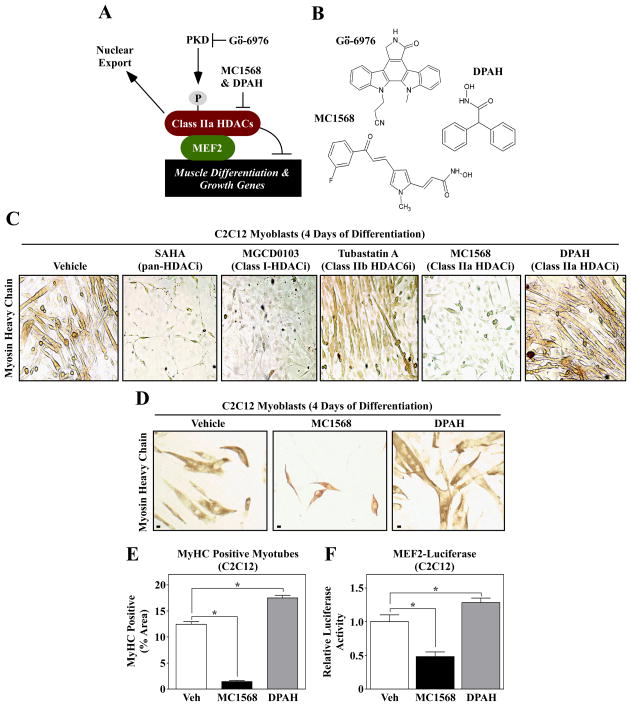
Fig. 1.
Differential effects of isoform-selective HDAC inhibitors on skeletal muscle differentation. (A) A schematic representation of the PKD-class IIa HDAC axis. Gö-6976 blocks the catalytic activity of PKD, while MC1568 and DPAH inhibit the enzymatic activity of class IIa HDACs. (B) The molecular structures of the compounds used in this study are shown. (C) C2C12 myoblasts were induced to differentiate in the absence (vehicle) or presence of the indicated HDAC inhibitors; SAHA (1 μM), MGCD0103 (500 nM), Tubastatin A (1 μM), MC1568 (10 μM) and DPAH (10 μM). After four days of differentiation, cells were fixed and stained with an anti-myosin antibody to reveal myosin heavy chain (MyHC)-positive skeletal myotubes. (D) C2C12 cells were induced to differentiate in the absence or presence of the class IIa HDAC inhibitors MC1568 and DPAH, stained as described for (C), and differentiation was quantified (E); Scale bar = 10 μm. (F) C2C12 myoblasts were transfected with a MEF2-dependent luciferase reporter gene, and the cells were subsequently induced to differentiate for three days in the absence or presence of MC1568 or DPAH. For (E) and (F), five independent plates of cells were analyzed per condition. Numbers represent averages +SEM; *P < 0.05 vs. vehicle-treated cells.