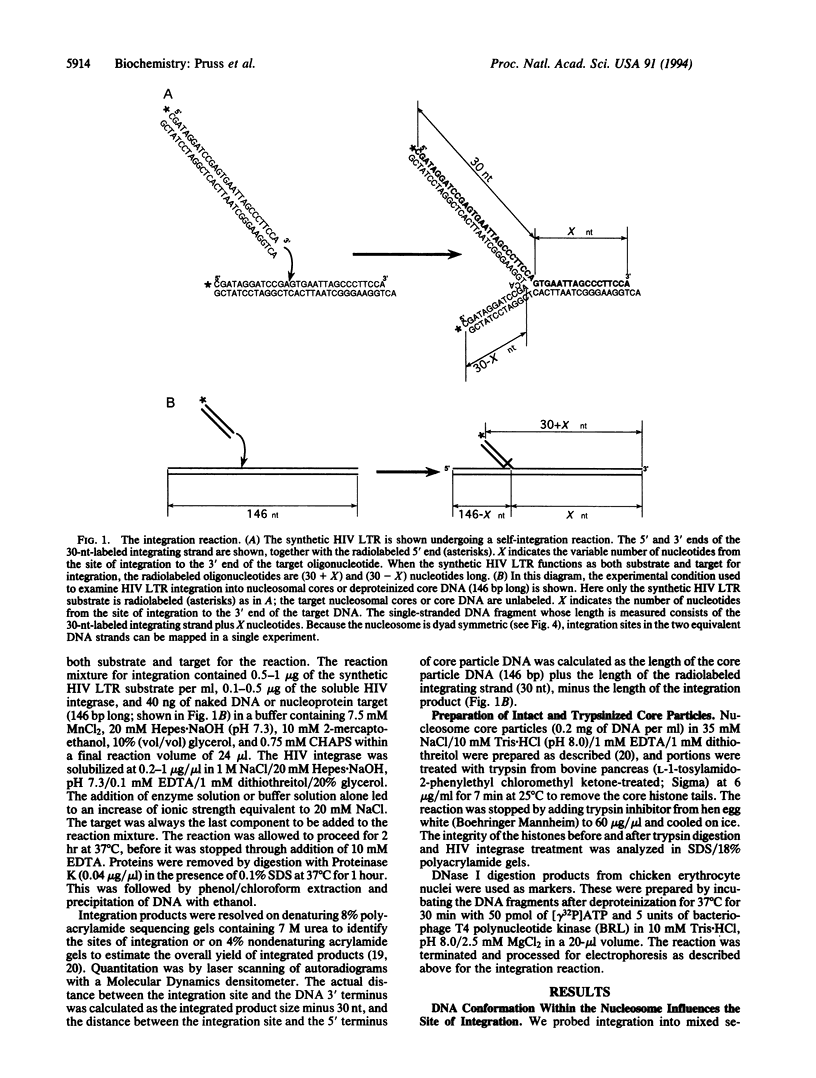
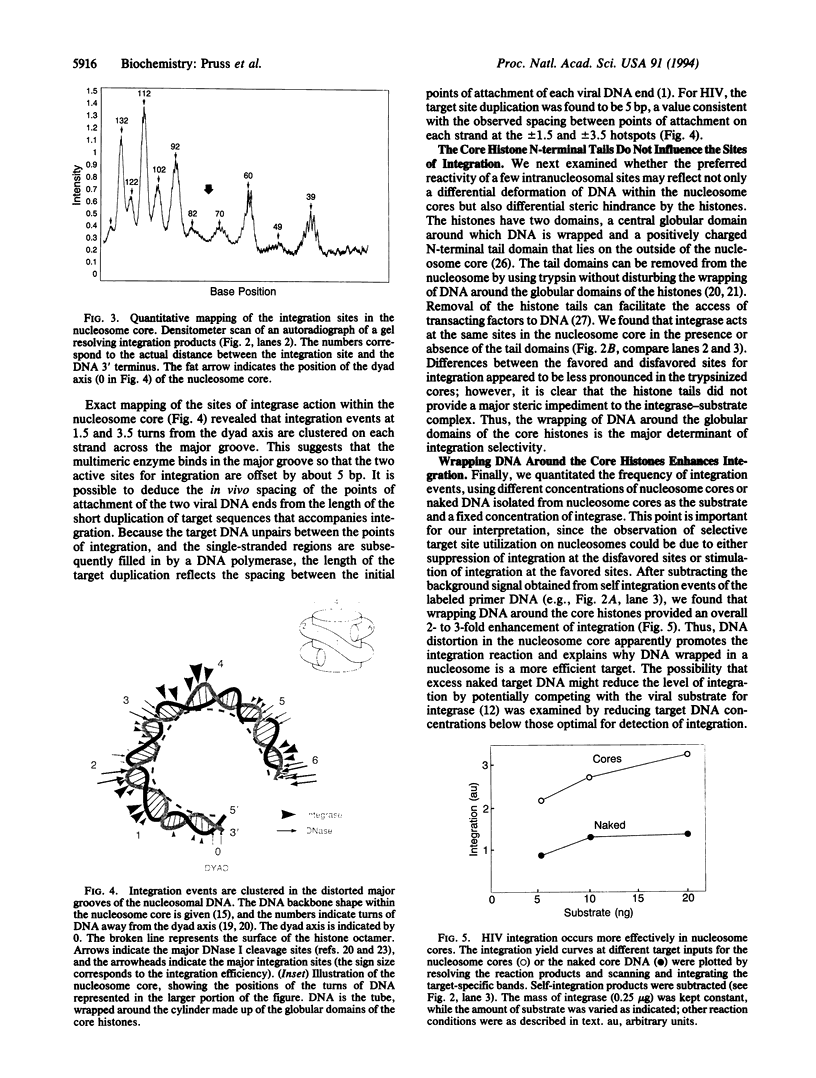
Abstract
We have examined the consequences of DNA distortion and specific histone-DNA contacts within the nucleosome for integration mediated by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-encoded integrase enzyme. We find that sites of high-frequency integration cluster in the most severely deformed, kinked DNA regions within the nucleosome core. This may reflect either a preference for a wide major groove for association of the integrase or a requirement for target DNA distortion in the DNA strand transfer mechanism. Both the distortion and folding of the target DNA through packaging into nucleosomes may influence the selection of HIV integration sites within the chromosome.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arents G., Burlingame R. W., Wang B. C., Love W. E., Moudrianakis E. N. The nucleosomal core histone octamer at 3.1 A resolution: a tripartite protein assembly and a left-handed superhelix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10148–10152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausio J., Dong F., van Holde K. E. Use of selectively trypsinized nucleosome core particles to analyze the role of the histone "tails" in the stabilization of the nucleosome. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 5;206(3):451–463. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90493-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Craigie R. Activities of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) integration protein in vitro: specific cleavage and integration of HIV DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1339–1343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Fujiwara T., Craigie R. Retroviral DNA integration directed by HIV integration protein in vitro. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1555–1558. doi: 10.1126/science.2171144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. Dodging the genes. Curr Biol. 1993 Aug 1;3(8):533–535. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(93)90050-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalker D. L., Sandmeyer S. B. Ty3 integrates within the region of RNA polymerase III transcription initiation. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):117–128. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Fujiwara T., Bushman F. The IN protein of Moloney murine leukemia virus processes the viral DNA ends and accomplishes their integration in vitro. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):829–837. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90126-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R. Hotspots and warm spots: integration specificity of retroelements. Trends Genet. 1992 Jun;8(6):187–190. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90223-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick F. H., Klug A. Kinky helix. Nature. 1975 Jun 12;255(5509):530–533. doi: 10.1038/255530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. The formation and function of DNase I hypersensitive sites in the process of gene activation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19259–19262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. J., Clark D. J., Wolffe A. P. Histone contributions to the structure of DNA in the nucleosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6829–6833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. J., Tullius T. D., Wolffe A. P. The structure of DNA in a nucleosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7405–7409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan M. E., Rooney T. F., Austin R. H. Evidence for kinks in DNA folding in the nucleosome. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):554–557. doi: 10.1038/328554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji H., Moore D. P., Blomberg M. A., Braiterman L. T., Voytas D. F., Natsoulis G., Boeke J. D. Hotspots for unselected Ty1 transposition events on yeast chromosome III are near tRNA genes and LTR sequences. Cell. 1993 Jun 4;73(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90278-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. Y., Hayes J. J., Pruss D., Wolffe A. P. A positive role for histone acetylation in transcription factor access to nucleosomal DNA. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90051-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutter L. C. Kinetic analysis of deoxyribonuclease I cleavages in the nucleosome core: evidence for a DNA superhelix. J Mol Biol. 1978 Sep 15;124(2):391–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90306-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooslehner K., Karls U., Harbers K. Retroviral integration sites in transgenic Mov mice frequently map in the vicinity of transcribed DNA regions. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3056–3058. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3056-3058.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryciak P. M., Müller H. P., Varmus H. E. Simian virus 40 minichromosomes as targets for retroviral integration in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):9237–9241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.9237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryciak P. M., Sil A., Varmus H. E. Retroviral integration into minichromosomes in vitro. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):291–303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05052.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryciak P. M., Varmus H. E. Nucleosomes, DNA-binding proteins, and DNA sequence modulate retroviral integration target site selection. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):769–780. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90289-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond T. J., Finch J. T., Rushton B., Rhodes D., Klug A. Structure of the nucleosome core particle at 7 A resolution. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):532–537. doi: 10.1038/311532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohdewohld H., Weiher H., Reik W., Jaenisch R., Breindl M. Retrovirus integration and chromatin structure: Moloney murine leukemia proviral integration sites map near DNase I-hypersensitive sites. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):336–343. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.336-343.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherdin U., Rhodes K., Breindl M. Transcriptionally active genome regions are preferred targets for retrovirus integration. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):907–912. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.907-912.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C. C., Stoye J. P., Coffin J. M. Highly preferred targets for retrovirus integration. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):531–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90569-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijaya S., Steffen D. L., Robinson H. L. Acceptor sites for retroviral integrations map near DNase I-hypersensitive sites in chromatin. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):683–692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.683-692.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. New insights into chromatin function in transcriptional control. FASEB J. 1992 Dec;6(15):3354–3361. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.15.1464369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]