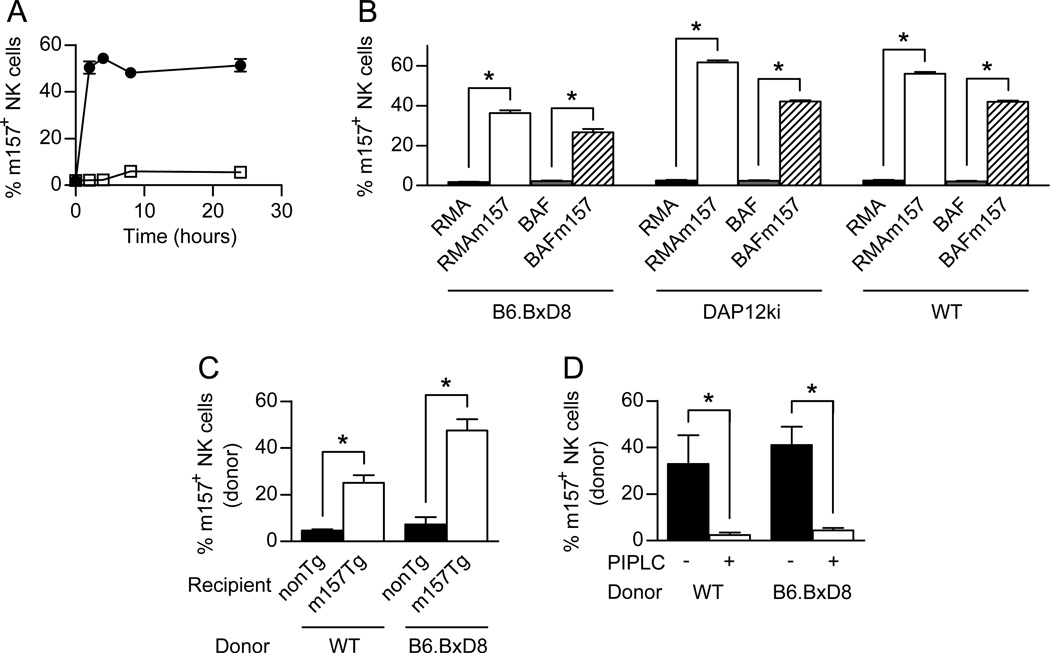
Figure 4. Acquisition of m157 occurs with fresh NK cells and in vivo.
(A) WT splenocytes were incubated with RMA (□) or RMAm157 (●) cells and assessed by flow cytometry for the percentage of NK (NK1.1+, CD3−) cells that were positive for m157 on their cell surface at various time points. (B) Splenocytes from B6.BxD8, DAP12ki or WT mice were incubated with RMA (black), RMAm157 (white), BaF (gray) or BaFm157 (hatched) cells for 2 hours and assessed by flow cytometry for the percentage of NK (NK1.1+, CD3−) cells that were positive for m157 on their cell surface (n= 6 for all groups except for WT with RMA or RMAm157 where n=3). (C) Adoptive transfer of 50 million WT or B6.BxD8 donor splenocytes into non-Tg (black) and m157-Tg (white) recipient mice. Donor NK cells were assessed by flow cytometry for the acquisition of m157 on their cell surface (n=5–17). (D) WT and B6.BxD8 donor NK cells were obtained 24 hours post transfer into m157-Tg recipient mice (n=4–5). The percentage of NK cells expressing m157 was assessed by flow cytometry before (black) and after treatment with PI-PLC (white). All data are presented as the mean+/− SEM. *p<0.005.