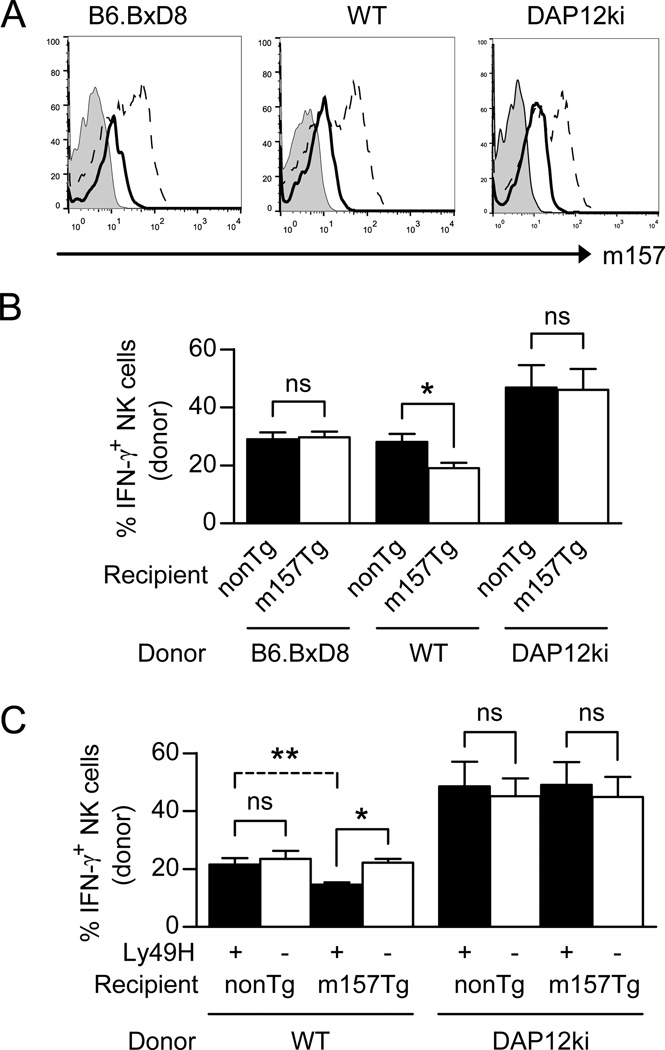
Figure 6. Expression of the Ly49H receptor is required to induce NK cell hyporesponsiveness.
(A) Representative histograms displaying m157 expression, as assessed by flow cytometry, on donor NK cells from either B6.BxD8, WT or DAP12ki mice injected into non-Tg recipient (tinted histogram) or into m157-Tg recipient mice (open histogram with solid line). The expression of m157 on NK cells from m157-Tg recipient mice is also shown (open histogram with dashed line). (B) B6.BxD8, WT, or DAP12ki splenocytes were injected into WT (black) or m157-Tg (white) recipient mice (n=5–6). Splenocytes were isolated at 2–3 days post transfer and assessed for IFN-γ production by donor NK cells following stimulation through the NK1.1 receptor. All data are presented as the mean+/− SEM. *p<0.02, ns=not significant. (C) WT or DAP12ki splenocytes were injected into WT or m157-Tg recipient mice (n=5–6). Splenocytes were isolated at 2–3 days post transfer and assessed for IFN-γ production by donor Ly49H+ NK cells (black) or donor Ly49H− NK cells (white) following stimulation through the NK1.1 receptor. All data are presented as the mean+/− SEM.*p<0.0005, **p<0.005, ns=not significant.