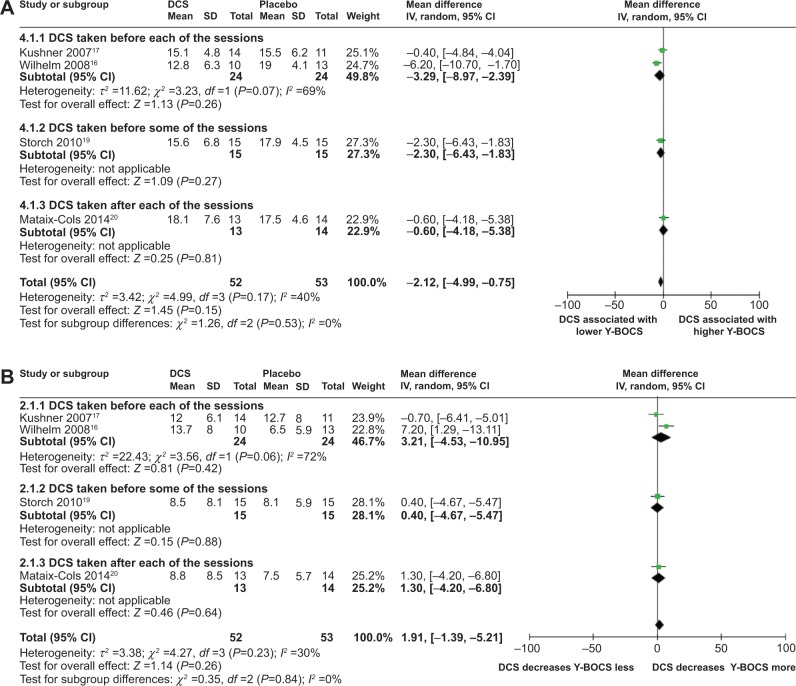
Figure 2.
Forest plots of the effect of DCS versus placebo on Y-BOCS value or on deceasing Y-BOCS values of the patients receiving behavioral therapy at midtreatment.
Notes: (A) Forest plot of comparison of the effect of the DCS and placebo on the Y-BOCS value of the patients receiving behavioral therapy at midtreatment; overall effect for continuous outcome (random-effect model). The diamond stood for pooled effect. No significant difference between the effect of DCS and placebo on Y-BOCS value of the patients receiving behavioral therapy at midtreatment, although DCS-augmented behavioral therapy showed a trend toward significantly lower Y-BOCS value compared to placebo-augmented behavioral therapy. (B) Forest plot of comparison of the effect of DCS and placebo on decreasing Y-BOCS of the patients receiving behavioral therapy at midtreatment; overall effect for continuous outcome (random-effect model). The diamond stood for pooled effect. No significant difference between the effect of DCS and placebo on decreasing Y-BOCS of the patients receiving behavioral therapy at midtreatment, although DCS-augmented behavioral therapy showed a trend toward significantly greater Y-BOCS decrease compared to placebo-augmented behavioral therapy.
Abbreviations: DCS, D-cycloserine; Y-BOCS, Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale; CI, confidence interval; SD, standard deviation; IV, inverse variance; df, degrees of freedom.