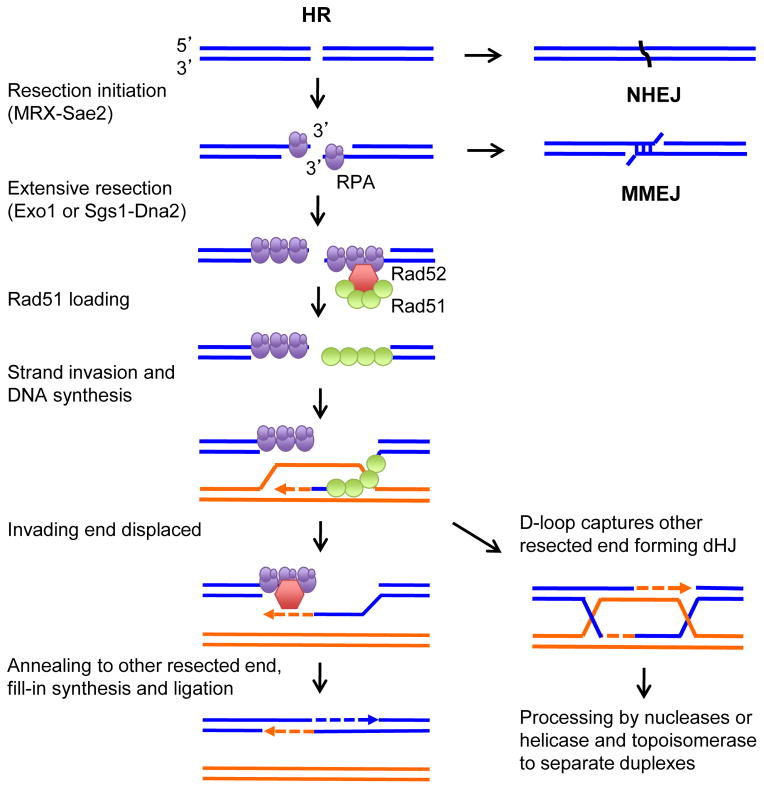
Figure 2.
Models for DSB repair. The DNA ends can be ligated by NHEJ or undergo resection to form 3′ ssDNA tails. The initial processing of the DNA ends has the potential to reveal short homologies internal to the ends that can be used for MMEJ. The long ssDNA tails are initially bound by RPA, which is then replaced by Rad51 with the assistance of Rad52 (or BRCA2). Rad51 promotes invasion of a donor duplex and the 3′ end is extended by DNA synthesis. The extended invading strand can be displaced by a helicase and can pair with the other resected end; alternatively, the displaced strand from the donor duplex pairs with the other break end and after gap filling and ligation a double Holliday junction (dHJ) intermediate is formed. The dHJ is acted on by a helicase and topoisomerase to dissolve the dHJ forming non-crossover products or cleaved by nucleases to generate crossover or non-crossover products.