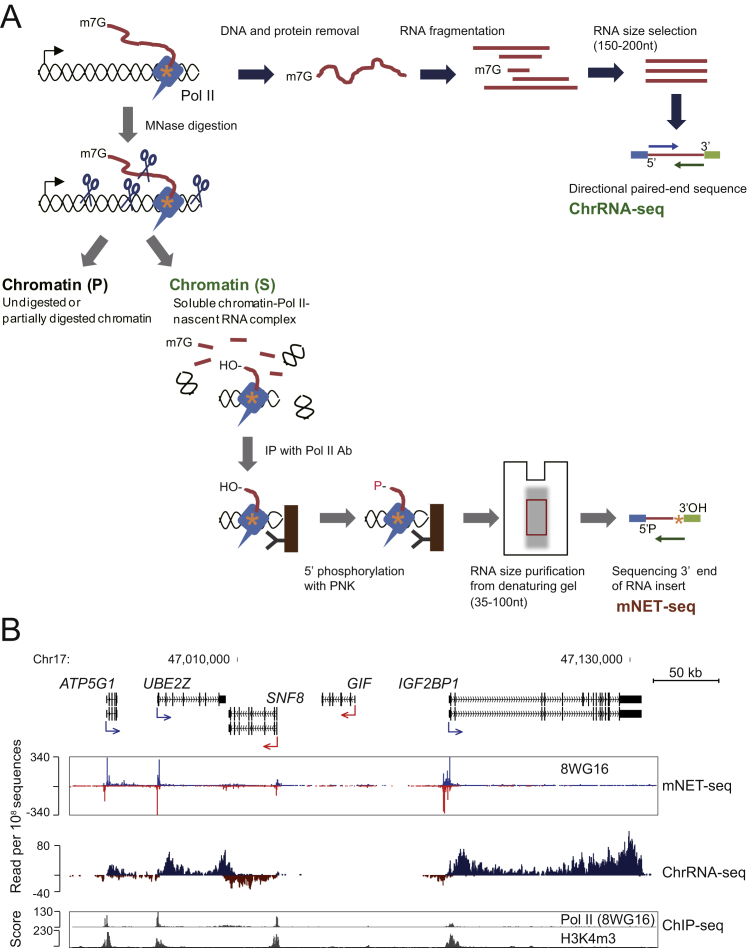
Figure S1.
Detailed ChrRNA-Seq and mNET-Seq Methods, Related to Figure 1
(A) (Above) ChrRNA-seq method. Pol II and RNA synthesis site are diagrammed as tailed blue box and orange asterisk, respectively. Chromatin-bound RNA (red line) is purified from isolated chromatin fraction by DNase and proteinase K treatments. RNA is fragmented to 150–200 nt and adapters ligated on both ends for paired-end 51bases directional deep sequencing (blue and green arrows).
(Below) mNET-seq method. Chromatin DNA and chromatin-bound RNA are digested with MNase I (light blue scissors). To separate insoluble pellet (P) and soluble chromatin supernatant (S), digested chromatin is centrifuged. Soluble Pol II-nascent RNA complex is immunoprecipitated (IP) with Pol II antibody. 5′ hydroxyl (OH) is then phosphorylated with PNK on beads and phenol extraction performed to remove DNA and proteins. IPed RNA is purified from denaturing gel (size range 35–100 nt). RNA adapters are added to both ends strand-specifically and deep sequencing is conducted from reverse sequence primer (green arrow) to read 3′ end of insert (orange asterisk).
(B) Example of mNET-seq and ChrRNA-seq data view on human chromosome 17. mNET-seq and ChrRNA-seq reads on the plus strand, blue and dark blue, respectively; mNET-seq and ChrRNA-seq reads on the minus strand, red and dark red, respectively. ChIP-seq (Pol II [8WG16] and H3K4m3) data are from the ENCODE project data sets (Consortium et al., 2012).