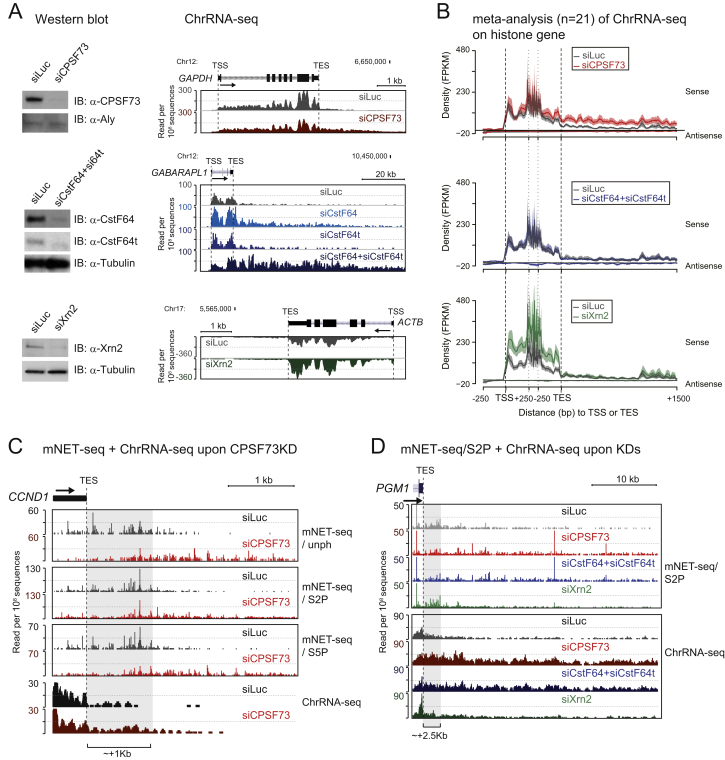
Figure S6.
mNET-Seq and ChrRNA-Seq Profiles upon CPA Factors and Xrn2 Knockdown, Related to Figure 6
(A) Termination defect on pA+ protein-coding genes. Western blots showing knockdown efficiencies of siRNA treatments for CPSF73, CstF64, CstF64t, and Xrn2. Aly and Tubulin proteins are loading controls (left). Termination defect detected following depletion of CPSF73 protein (red) on GAPDH (right top). Additive termination defect seen following double-knockdown of CstF64 and CstF64t (turquoise and blue and dark blue double) on GABARAPL1 (right middle). No termination defect detected following Xrn2 depletion (green) on ACTB (right bottom).
(B) mNET-seq meta-profile on histone gene upon CPA factors and Xrn2 knockdown. Effect of siCPSF73 (red, top), siCstF64+siCstF64t (blue, middle), and siXrn2 (green, bottom). n = 21. Line and shading represent mean ± SEM for each bin.
(C) TES of CCND1 as an example of mNET-seq with three different Pol II antibodies (top) and ChrRNA-seq (bottom) from siLuc (control siRNA, dark gray) and siCPSF73 (red) treated HeLa cells. Grey shaded region shows the decrease of Pol II density in siCPSF73-treated cells.
(D) TES of PGM1 as an example of mNET-seq/S2P (top) and ChrRNA-seq (bottom) from siLuc (control siRNA, dark gray), siCPSF73 (red), siCstF64+siCstF64t (blue), and siXrn2 (green) treated HeLa cells. Grey shaded region shows the decrease of Pol II density in siCPSF73 and siCstF64+siCstF64t-teated cells.