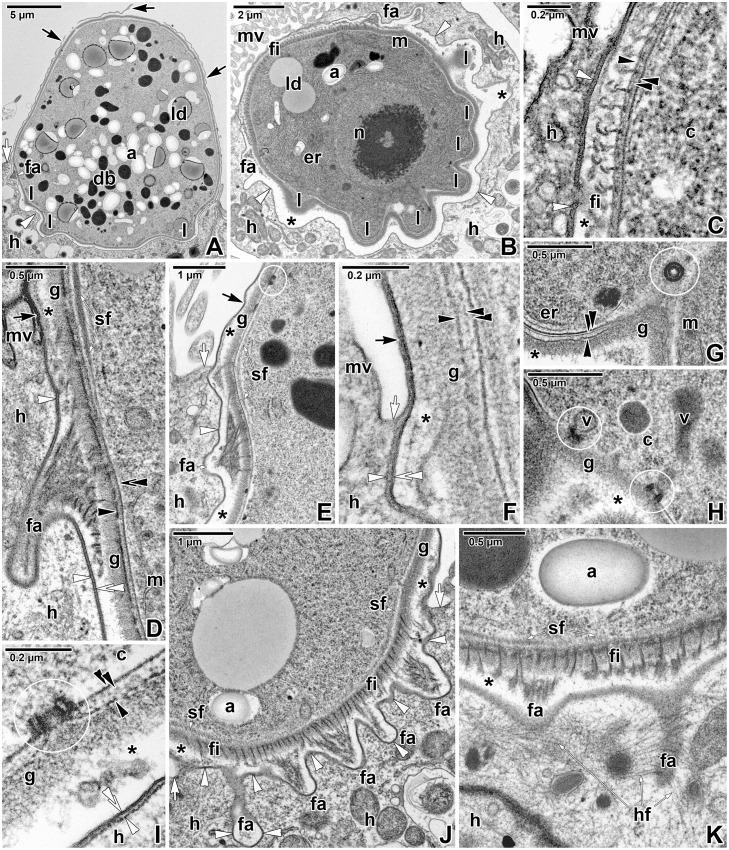
Fig 6. Fine structure of the attachment site of Eleutheroschizon duboscqi gamonts.
A. Macrogamont with a ruptured PS. TEM. B. Oblique section of the attachment site. TEM. C. A detail showing the hook-shaped short filaments anchored into the parasite outer cytomembrane. TEM. D-E. The attachment fascicles in a longitudinal section. The subpellicular layer of filaments is localised just beneath the parasite IMC and ends above the fascicles. TEM; D is stained with RR. F. The annular joint point of two host membranes. TEM. G. A detail of the attachment lobe packed with endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria. Note the cross-sectioned micropore. TEM. H. Detailed view of vesicles connected with the micropores located in the area of attachment lobes. TEM. I. Longitudinal section of a micropore localised at the parasite attachment site. TEM. J. Detailed view of the attachment fascicles of long filaments alternating with short filaments. TEM. K. The basal part of PS showing an accumulation of fine filaments in the host cell cytoplasm surrounding the PS invaginations with attachment fascicles. TEM, RR. a—parasite amylopectin, asterisk—space between the parasite and PS, black arrow—PS, black arrowhead—parasite plasma membrane, black double/paired arrowheads—parasite cytomembranes, c—parasite cytoplasm, db—parasite dense bodies, er—parasite endoplasmic reticulum, fa—attachment fascicle of filaments, fi—short attachment filaments, g—glycocalyx, h—host cell, hf—filaments in host cell cytoplasm, l—attachment lobe, ld—parasite lipid droplets, m—parasite mitochondria, mv—microvilli and cilia of the host enterocyte, n—parasite nucleus, sf—parasite subpellicular filaments, v—parasite vesicle, white arrow—host cell plasma membrane, white arrowhead—dense band, white double arrowhead—base of the PS. Micropores are indicated by white circles.