Fig. 1. Flowchart of HBV testing on 2048 HIV-infected, pregnant women screened for the Breastfeeding, Antiretrovirals, and Nutrition study.
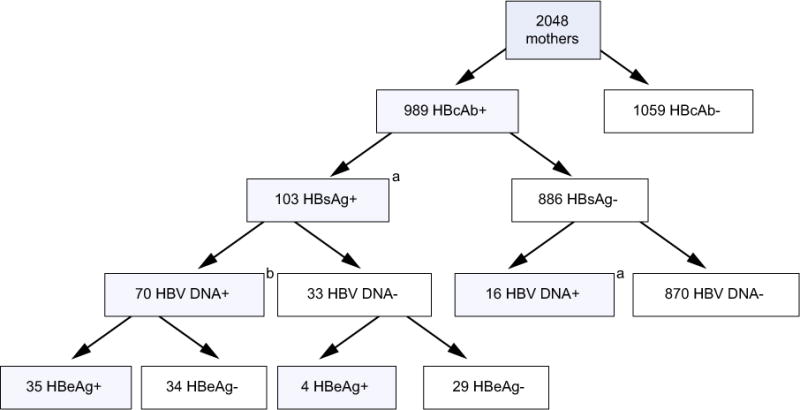
aInfant testing for hepatitis B was limited to infants born to HBsAg-positive (n = 103) or HBsAg-negative and HBV-DNA-positive (n = 16) mothers at the screening visit who enrolled in BAN at delivery (n = 95) and whose infants remained HIV-negative at 2 weeks of life (n = 79) and had plasma specimens available for HBV testing at 2 weeks (n = 57) and/or 48 weeks (n = 51) of age for a total of 72 infants tested for hepatitis B. These infants were included in the analysis of HBV infection among infants (Table 1). bVolume insufficient for HBeAg testing of one mother and for determining HBV DNA concentration in another mother.
