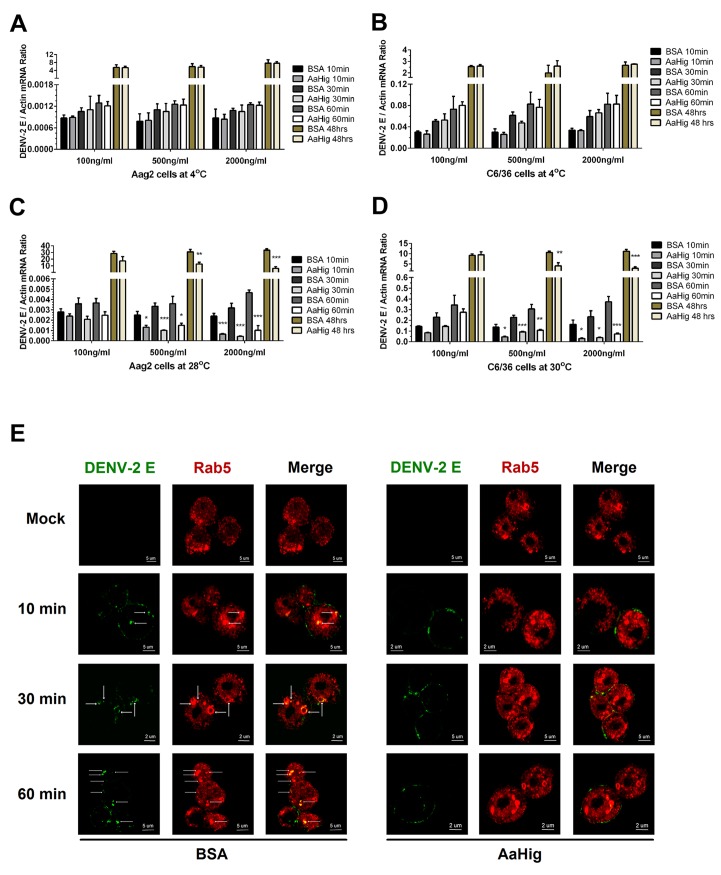
Fig 8. AaHig interrupts flaviviral endocytosis into mosquito cells.
(A-B) Viral attachment assay. The serial concentration of purified AaHig protein was premixed with 5 M.O.I. DENV-2 on ice, and then the Aag2 (A) and C6/36 (B) cells were consequently preadsorbed with the mixture for a time course at 4oC. The cells were washed 5 times by cold PBS and collected at certain time points for total RNA isolation. (C-D) Viral entry assay. The serial concentration of purified AaHig protein was premixed with 5 M.O.I. DENV-2 on ice, and then the mixture was transferred into the cultured Aag2 cells (C) at 28°C and C6/36 (D) cells at 30°C respectively. The cells were stringently washed 5 times by PBS at room temperature, and then collected at serial time points for detection. (A-D) For the assay at 48 hours, the cells were washed 5 times after 1 hr incubation at 4°C (A and B) or 28°C /30°C (C and D), and consequently cultured at 28°C (Aag2) or 30°C (C6/36) for an additional 48 hrs. The viral genome was determined by Taqman qPCR and normalized by A. aegypti actin. The data were presented as the mean ± standard error. The result was combined from 3 independent experiments. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001. (E) Detection of AaHig-mediated entry interruption by structured illumination microscopy imaging. The Aag2 cells were seeded in a class bottle cell culture dish. The purified AaHig protein premixed with 10 M.O.I. DENV-2 was added into the cells. The equal amount of BSA was used as a negative control. The treated cells were collected and analyzed at a time course. DENV-2 was stained by the 4G2 mouse mAb and anti-mouse IgG Alexa Fluor-488 (Green). The early endosome marker, Rab5, was stained by a rabbit polyclonal antibody and anti-rabbit IgG Alexa Fluor-546 (Red). Images were examined using the 100×objective lens of a Zeiss ELYRA PS.1 structured illumination microscopy.