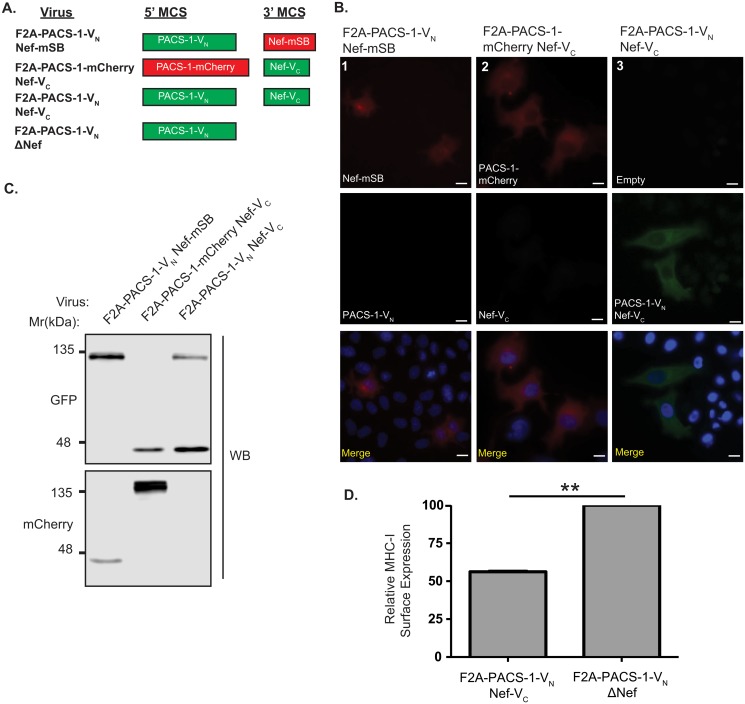
Fig 4. Visualizing the Nef/PACS-1 interaction using viral Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation.
(A) Schematic representation of proteins produced from lentiviral expression system. (B) HeLa cells were infected with various viruses encoding different fusion proteins and visualized using widefield fluorescence microscopy. BiFC (green, column 3) was visualized in the F2A-PACS-1-VN Nef-VC infected HeLa cells and not the control BiFC viral infections (columns 1 and 2). Cells were mounted in DAPI Fluoromount G media for nuclear staining (blue). Scale bars represent 15μm. (C) Expression of the VN or VC fragment was detected by a GFP specific Western blot, whereas the mCherry and mSB fusions, which acted as controls, were detected by an mCherry specific western blot. Densitometry measurements for PACS-1-VN and Nef-VC were 10,500 and 29,200 arbitrary units, respectively, as determined by Licor C-Digit. (D) Jurkat E6.1 T-cells were infected with F2A-PACS-1-VN Nef-VC and the corresponding non-functional Nef mutant (F2A-PACS-1-VN ΔNef). At 72 hours post infection, cells were surface stained for MHC-I (W6/32 antibody), fixed, permeabilized and stained for intracellular p24 (KC57-RD1 antibody). Columns represent relative MHC-I surface expression calculated from the geometric mean fluorescent intensity (gMFI) of surface MHC-I on infected cells and normalized to cell surface MHC-I levels of ΔNef-infected cells. Error bars were calculated from four independent repeats. (* indicates p-value < 0.01).