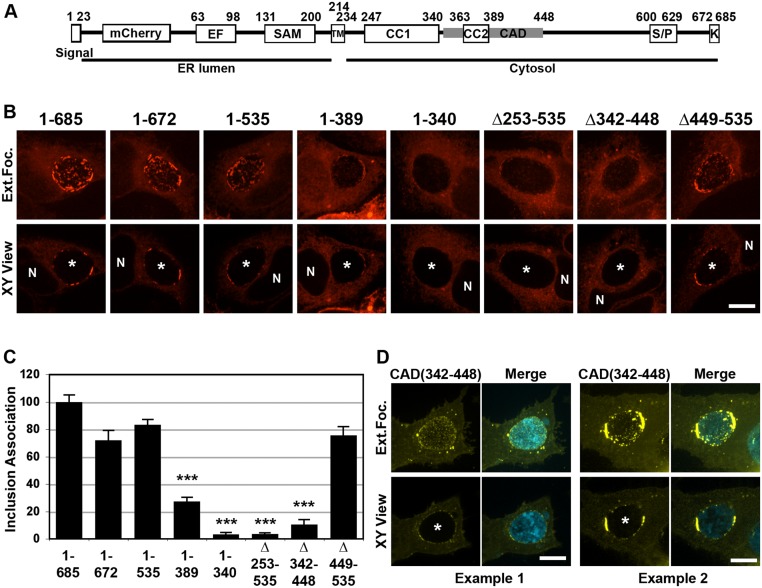
Fig 7. The CAD domain of STIM1 is required for STIM1 localization to ER-Inclusion MCSs.
A. Schematic representation of the major domains of the STIM1 protein, their respective amino acid residue position and their respective cellular localization (ER lumen or Cytosol). Signal: signal peptide; EF: EF-hand; SAM: sterile alpha motif; TM: transmembrane domain; CC1: coiled-coil 1; CC2: coiled-coil 2; CAD: CRAC activation domain; S/P: Serine-proline-rich region; K: lysine-rich region. B. Confocal micrographs of HeLa cells expressing the indicated mCherry-STIM1 construct (red) and infected with C. trachomatis for 24h. The top and bottom panels respectively correspond to the extended focus view combining all the confocal planes (Ext.Foc.) and a single plane crossing the middle of the inclusion (XY View). The asterisk in the XY View Merge panel indicates the inclusion and N indicates the nucleus. Scale bar: 10μm. C. Quantification of inclusion association of the indicated mCh-STIM1 constructs compared to full-length mCh-STIM1. *** p value <0.001. D. Confocal micrographs of HeLa cells expressing YFP-CAD (CAD(342–448), yellow), and infected for 24h with a strain of C. trachomatis expressing CFP (cyan). The merge is shown on the right. Two representative examples of YFP-CAD pattern on the inclusion are shown. The top and bottom panels respectively correspond to the extended focus view combining all the confocal planes (Ext.Foc.) and a single plane crossing the middle of the inclusion (XY View). The asterisk in the XY View Merge panel indicates the inclusion. Scale bar: 10μm.