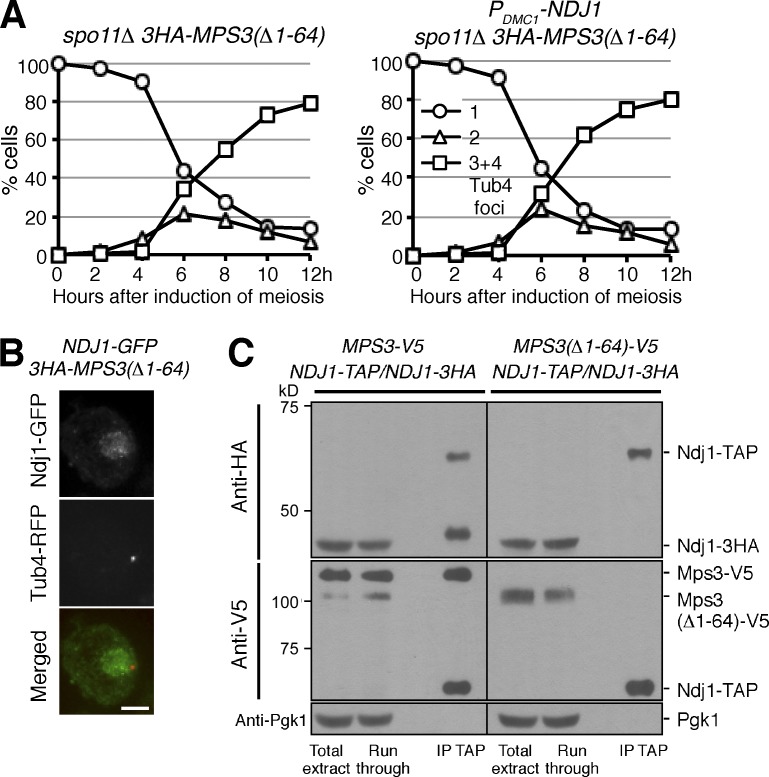
Figure 7.
Mps3 is the target of Ndj1 at the SPB during yeast meiosis. (A) Removal of the N terminus of Mps3 abolishes the Ndj1 activity at the SPB. Yeast cells (HY4864 and HY4865) were induced to undergo synchronous meiosis, and SPB separation was determined using fluorescence microscopy. Tub4-RFP was used as the SPB marker as in Fig. 3 B. The graphs shown are from a representative time-lapse experiment out of three repeats. (B) Localization of Ndj1 to SPB depends on the N terminus of Mps3 during yeast meiosis. Strain HY4865 was used. Ndj1-GFP, green; Tub4-RFP, red. Quantification of Ndj1 localization to SPB is shown in Fig. S2 C. Bar, 2 µm. (C) Ndj1 binds to the N terminus of Mps3. Yeast strains MPS3-V5/MPS3-V5 NDJ1-TAP/NDJ1-TAP (HY4393) and MPS3(Δ1-64)-V5/MPS3(Δ1-64)-V5 NDJ1-TAP/NDJ1-3HA (HY4412) were induced to undergo synchronous meiosis. Cells were collected 4.5 h after meiosis and prepared for TAP affinity purification. Note that Ndj1-3HA is copurified with Ndj1-TAP only in the presence of the full length of Mps3. The level of Pgk1 serves as a negative control.