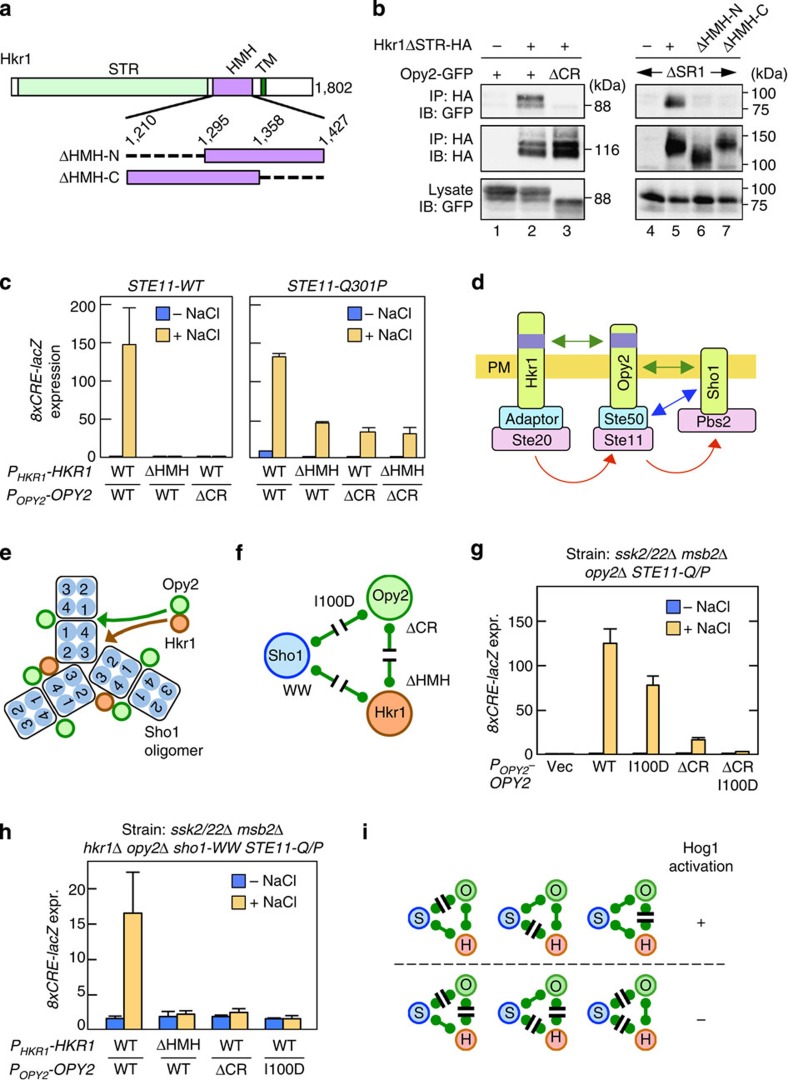
Figure 10. The roles of the Sho1–Opy2–Hkr1 interactions in osmotic activation of Hog1.
(a) Schematic model of Hkr1. Structures of the HMH domain deletion mutants are enlarged. Numbers are amino-acid positions. (b) Opy2–Hkr1-binding assay. The indicated Hkr1 and Opy2 constructs were expressed in TM257 (left) or QG158 (right) strains. Cell lysates were prepared with Buffer A containing 1% digitonin. Hkr1ΔSTR-HA was immunoprecipitated, and co-precipitated Opy2-GFP was detected by immunoblotting. (c) Hog1-specific reporter assays of KY585 and KY599-2 strains co-transfected with the indicated Hkr1 and Opy2 expression plasmids. Cells were stimulated with or without 0.4 M NaCl for 30 min, and the expression of the 8xCRE-lacZ reporter gene was determined. Error bars are s.d. (n⩾3). (d) Schematic model of sequential interaction among Hkr1, Opy2 and Sho1. (e) Summary of the interactions among Sho1, Opy2 and Hkr1. Only a portion of the Sho1 oligomer is shown. (f) Mutations that disrupt the interactions between Sho1, Opy2 and Hkr1. (g–h) Hog1-specific reporter assays of the yeast strains AN004 (g) and KY602-12 (h) transformed with expression plasmids for the indicated mutants of Opy2 and Hkr1 (native promoters). Cells were stimulated with or without 0.4 M NaCl for 30 min and expression of the 8xCRE-lacZ reporter gene was determined. Error bars are s.d. (n=4). (i) Summary of the functional effects of mutations that disrupt interactions between Sho1 (S), Opy2 (O) and Hkr1 (H).