Figure 1.
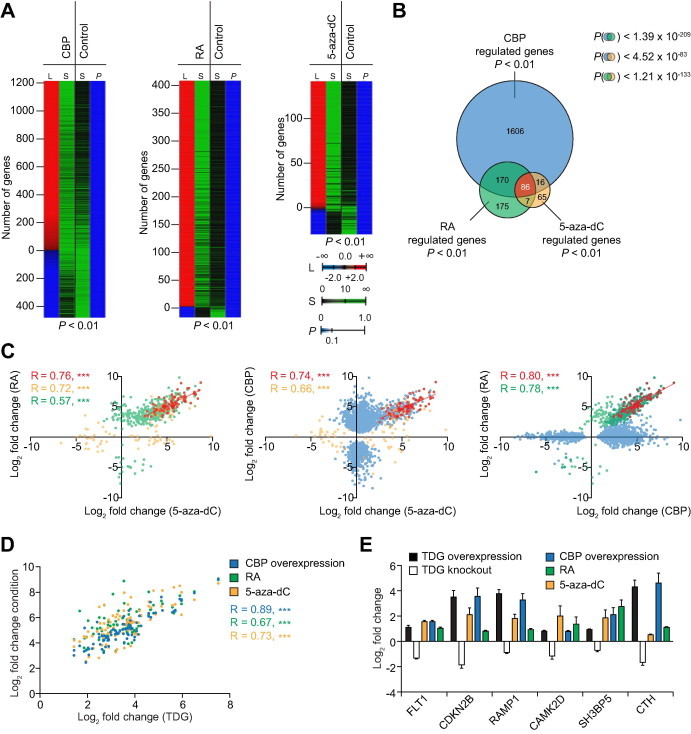
Comparison of CBP, 5-aza-dC and RA target genes by transcriptome profiling A. Heatmaps of a substraction profile of significantly (post hoc pFDR P < 0.01) regulated genes after CBP overexpression (left), RA treatment (middle) and 5-aza-dC treatment (right) of HEK293 cells. Mock transfected, ethanol- or DMSO-treated cells were used as controls, respectively. The number of genes (L, column 1) that are positively (red shading) and negatively (blue shading) regulated is shown together with the average over three independent biological replicate signals for each condition (S, column 2) and control (S, column 3). The final column (column 4) represents the post hoc P values (P). B. Venn diagram for the overlap of genes regulated in a statistically significant manner in all three conditions studied in A. The P values (hypergeometric distribution) for chance occurrence of each overlap are indicated. Note that the overall overlap of 86 genes is almost entirely composed of genes which are derepressed by 5-aza-dC treatment and concomittantly activated by atRA treatment and CBP overexpression. C. Scatter plots of the overlaps of methylation and RA-regulated genes (left), methylation and CBP-regulated genes (middle), and RA- and CBP- regulated genes (right) reveals clear Pearson’s correlations (R). Genes with expression significantly affected under both conditions compared in each panel are indicated in red. Genes with expression significantly affected upon CBP overexpression only (blue), by RA treatment only (green) and by 5-aza-dC treatment only (brown) are also indicated in different colors. ∗∗∗P < 0.001. D. Scatter-plot of the common subset from panel B in each condition (Y axis) compared to the overexpression of human TDG in HEK293 cells (X axis). E. Gene expression changes of an assigned set of the common subset from panel B in HEK293 cells overexpressing human TDG and in TDG knockout mouse embryonic fibroblasts [23]. TDG, thymine DNA glycosylase; RA, retinoic acid; 5-aza-dC, 5-azacytidine; FLT1, fls-related tyrosine kinase 1; CDKN2B, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2B; RAMP1, receptor activity modifying protein 1; CAMK2D, calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II delta; SH3BP5, SH3-domain binding protein 5; CTH, cystathionase.
