Figure 2.
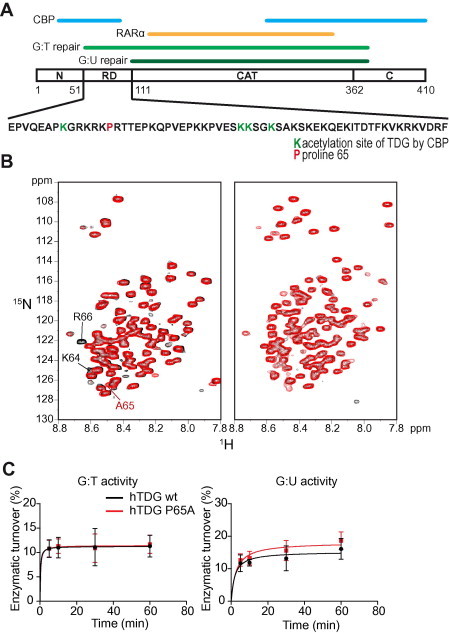
Structure and activity of wild type TDG and the mutant P65A A. Schematic structure of hTDG. The regions required for G:T and G:U mismatch recognition and processing (light and dark green, respectively), the N- and C-termini, the regulatory domain (RD), the catalytic (CAT) domain as well as the interfaces with CBP (blue) and RARα (brown) are indicated. The amino acid sequence of the RD is provided and the lysines that can be acetylated by CBP and the proline 65 that was mutated in this study are highlighted in green and red, respectively. B.1H–15N HSQC spectra of the N-terminus (amino acid residues 1–111) (left panel) and full length hTDG (right panel). Spectra for wild-type and the P65A mutant are shown in black and red, respectively. The resonances of the neighboring amino acids of P65 as well as the resonance of the introduced alanine are indicated. C. Glycosylase kinetics of human TDG wild-type and P65A mutant on G:T and G:U repair. DNA nicking assays were performed on a 25-mer dsDNA containing either a central G:T (left panel) or a G:U (right panel) mismatch. A 25-mer dsRNA containing a central canonical G:C pair was used as a control.
