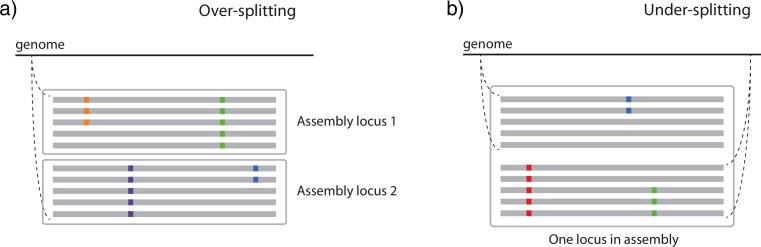
Figure 1. Two ways in which similarity thresholds can result in spurious assemblies.
(A) over-splitting occurs when reads from different alleles from the same genomic position are spuriously split into multiple loci due to lower similarity than the similarity threshold parameter, and (B) under-splitting occurs when reads from different genomic positions are clustered into a single locus due to higher similarity than the similarity threshold parameter. Gray bars represent identical sequence across reads, whereas colored squares represent alternate alleles at SNPs.