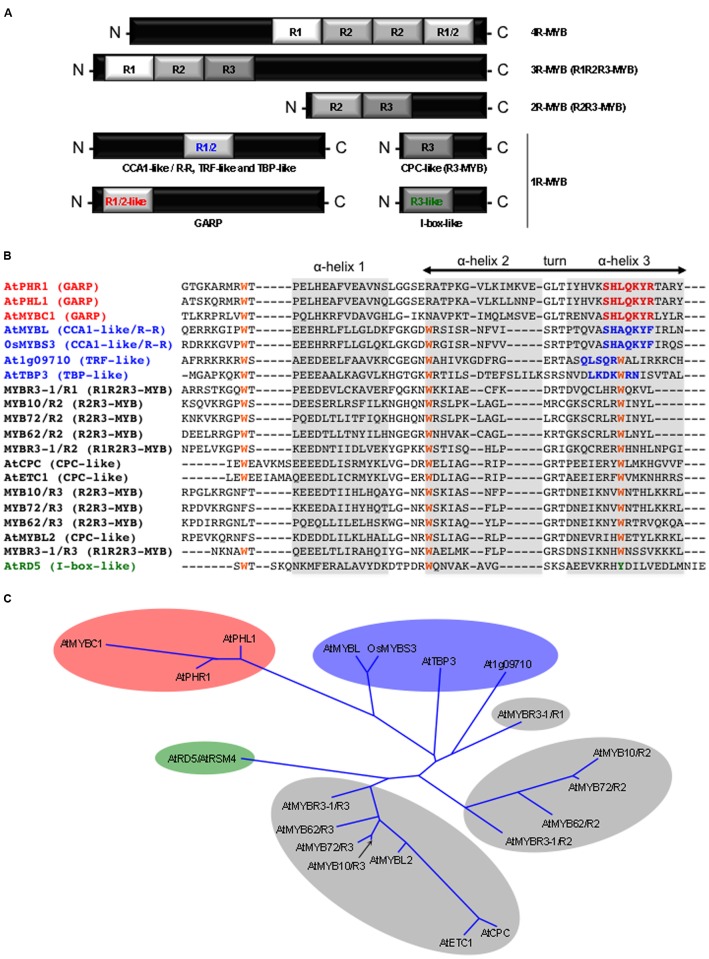
FIGURE 1.
The plant MYB protein family. (A) Schematic representation of the different MYB protein classes based on the number (from 1 to 4) and the type (i.e., R1, R2, R3, R1/2, R1/2-like, and R3-like) of adjacent MYB repeat (R). It must be noted that the position of the R1/2 MYB repeat alongside the polypeptide chain of the proteins may vary between the different 1R-MYB subclasses that contain this domain (i.e., CCA1-like/R-R, TRF-like, and TBP-like). (B) Sequence alignment of MYB repeats from different classes of MYB proteins. Conserved tryptophan (W) residues are highlighted in orange. Specific amino acid signatures of the GARP, the CCA1like/R-R, TRF-like, and TBP-like, and the I-box-like 1R-MYB classes are highlighted in red, blue, and green, respectively. α-Helices are shaded in gray. The α-helix 3 is the recognition helix that makes direct contacts with DNA nitrogen bases (i.e., interacting with cis-regulatory sequences). Protein sequences were downloaded from TAIR (except for OsMYBS3, GenBank: accession AAN63154). (C) Phylogenetic relationship (unrooted tree, neighbor joining method) between the different classes of MYB repeats. The corresponding protein name is given at the extremity of each branch of the tree. The GARP, the CCA1like/R-R, TRF-like, and TBP-like, and the I-box-like repeats are shaded in red, blue and green, respectively. R1, R2, and R3 repeats are shaded in gray. (Adapted from Stracke et al., 2001, Dubos et al., 2010, and Du et al., 2013).