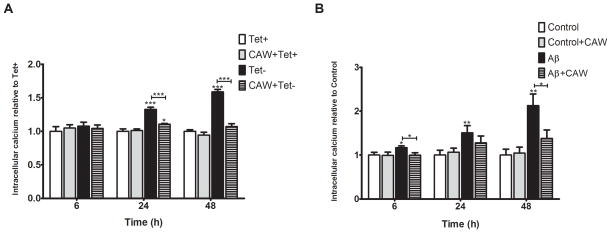
Figure 5. CAW treatment significantly attenuates Aβ-induced increases in intracellular calcium in MC65 and SH-SY5Y cells.
A) In MC65 cells there were no differences in intracellular calcium levels after 6 hours of treatment however, there was a significant increase in intracellular calcium at 24h in the absence of tetracycline (Tet−) which continued at 48h. CAW treatment significantly reduced the increase in calcium in the Tet− condition but had no effect on calcium levels in the presence of tetracycline (n=8 per treatment condition). B) Aβ treatment slightly increased intracellular calcium in SH-SY5Y cells after 6h, with progressively larger increases at 24h and 48h. CAW treatment (100ug/mL) prevented Aβ-induced increase at all time points. CAW treatment had no effect on intracellular calcium in the absence of Aβ. (n=10–12 per treatment condition). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 relative to either Tet+ or Control unless otherwise indicated.