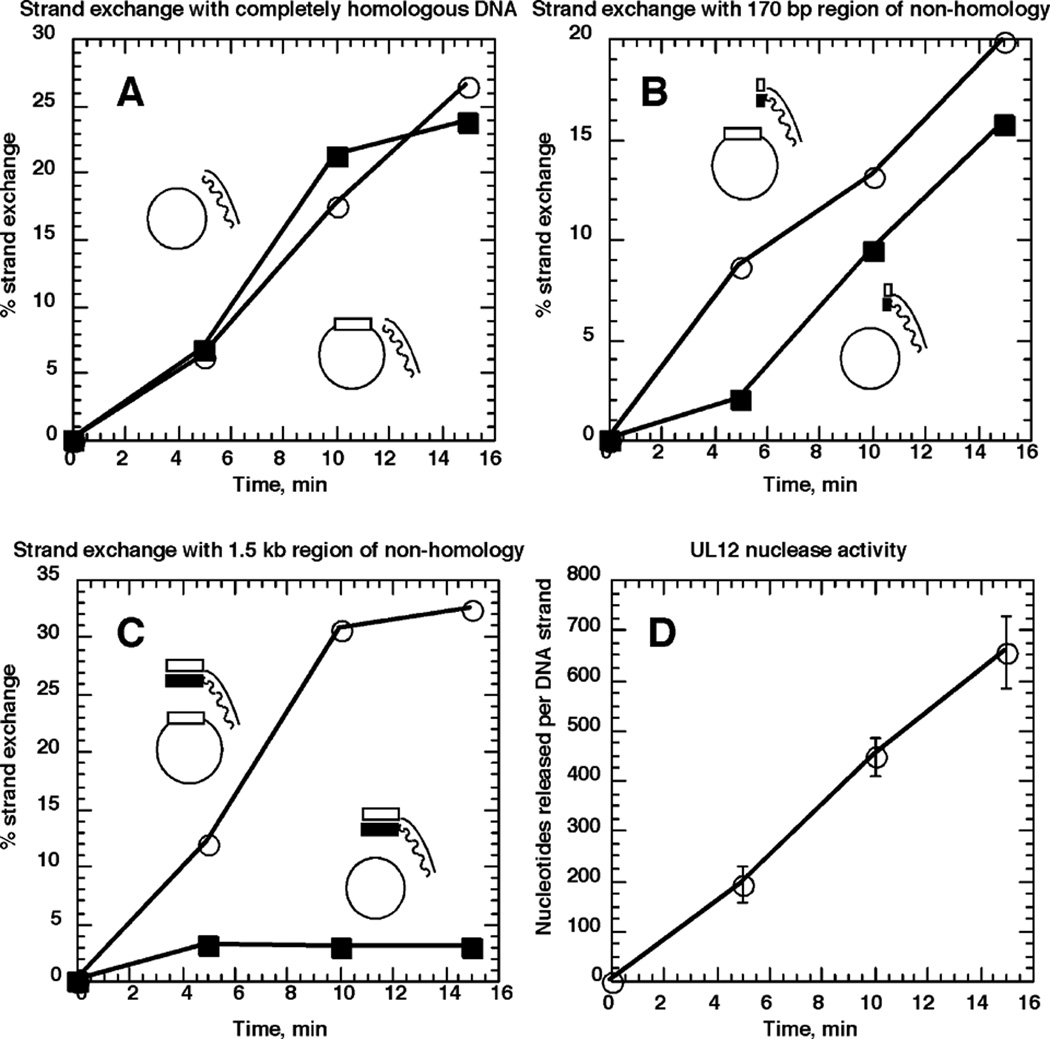
Figure 7.
Non-homology at the 3′ end of the pairing strand delays strand exchange. Strand exchange was performed by UL12 and ICP8 as described in Materials and Methods with either ssM13mp18 (filled squares) or ssM13wins (open circles). The dsDNA substrates used were prepared by PCR as 32P-labeled 3.5 kb fragments using M13wins as template. Both [α-32P]dCTP and [α-32P]dATP were used for labeling of this substrate. The 1.5 kb block of HSV-1 sequence, represented by rectangles, is at the 3′ end of the pairing strand, and the remaining 2 kb are M13mp18 sequence. The wavy line/filled rectangle represents the strand complementary to the ssDNA substrates. The 3.5 kb fragment was cut with BamHI to completely remove the 1.5 kb region of non-homology, and the 2 kb fragment was purified. This substrate was used in A. The 3.5 kb fragment was also cut with EcoNI, to create a substrate possessing 170 bases of DNA non-homologous to M13mp18. The 2.17 kb fragment was purified and used for strand exchange illustrated in B. In C, the full-length 3.5 kb fragment was used, which has 1.5 kb of DNA non-homologous to M13mp18. Percentage strand exchange was calculated as the percentage of radioactivity in slowly migrating species representing strand exchange products, out of the total radioactivity in the lane. Results are the averages of two independent experiments. D, The results of the nuclease digestion of the dsDNA substrates during the course of the strand exchange assay. Results are the averages of at least three DNA samples per time-point.