Fig. 4.
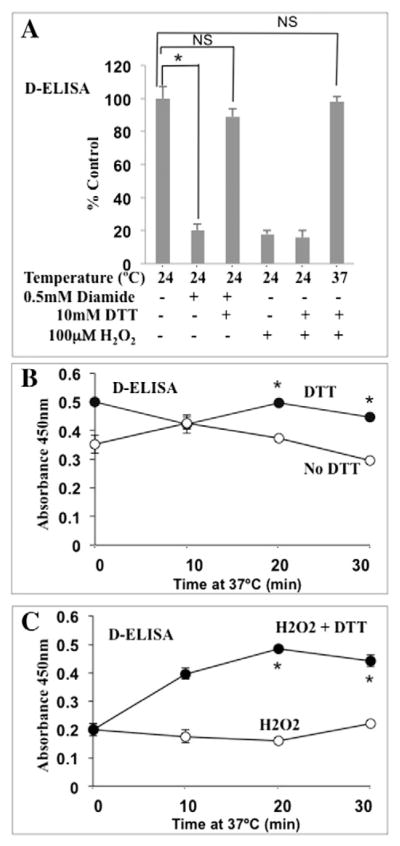
Redox regulation of RUNX2 DNA binding. (A) EC nuclear extracts were treated with diamide (15 min) to specifically oxidize Cys residues followed by reduction with DTT (15 min) at 24 °C. Diamide oxidation of Cys residues inhibited RUNX2 activity, which was reversible by DTT treatment at 24 °C (for untreated vs diamide, *p < 0.0015; for untreated vs diamide + DTT; NS, p < 0.06 m, not significant). H2O2 treatment (100 μM) inhibited DNA binding (p < 0.005), which was reversible only at 37 °C for 30 min (NS, p < 0.12; not significant relative to untreated). RUNX2-specific DNA binding was measured quantitatively by D-ELISA. (B) Comparison of RUNX2 DNA binding (triplicate determinations) in nuclear extracts incubated at 37 °C for 30 min. DTT (30 mM) prevented loss of RUNX2 activity. *p < 0.05 relative to no DTT. (C) Nuclear extracts treated with 100 μM H2O2 showed low DNA binding. Addition of DTT (30 mM) after H2O2 treatment restored DNA-binding activity within 20 min at 37 °C. *p < 0.05 relative to H2O2 alone.
