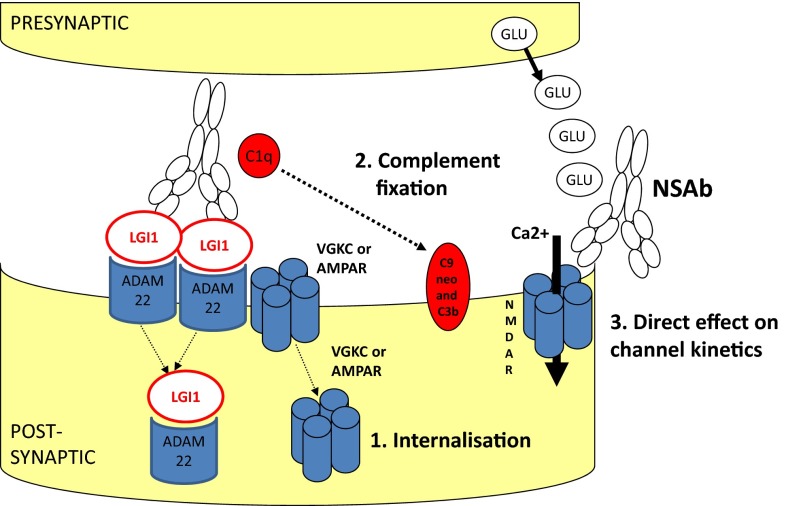
Fig. 4.
Potential pathogenic mechanisms of neuronal surface-directed antibodies (NSAbs). a Internalisation of receptors has been demonstrated in vitro using NMDAR (N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor), AMPAR (a-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptor) and GABAAR (γ-aminobutyric acid A receptor)-antibodies. Here the LGI1–ADAM22 interaction is shown as a possible unit for co-internalisation. b Antibody-mediated complement fixation and complement-mediated membrane receptor disruption as seen with antibodies against AQP4 (aquaporin-4). c Direct alteration of ion-channel molecular function is an alternative mechanism