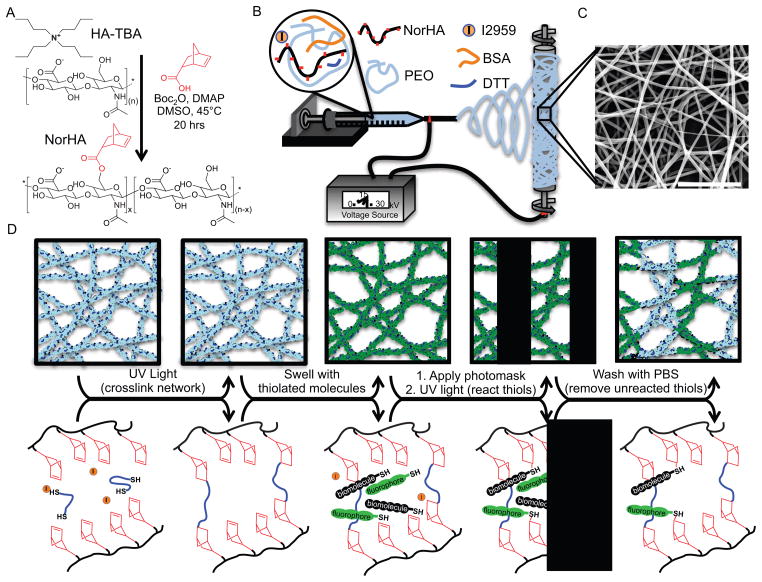
Figure 1.
Electrospun nanofibrous hydrogel formation, crosslinking, and biochemical ligand patterning. (A) Synthesis of norbornene-hyaluronic acid (NorHA) with norbornene group shown in red. (B) Electrospinning process and (C) morphology of nanofibers post electrospinning (Scale bar: 5μm). (D) Schematic illustrating gross fiber appearance (top row) and the corresponding molecular reactions (bottom row) associated with the steps to crosslink and pattern biochemical ligands in nanofibrous hydrogels. Crosslinking occurs in the dry state via UV light initiated thiol-ene reactions of a di-thiol and norbornene groups on NorHA (to stabilize the nanofibrous structure upon hydration). Subsequent patterning is achieved by exposing scaffolds to UV light through a photomask in the presence of a UV initiator and thiolated biomolecules to react with remaining norbornene groups.