Figure 11.
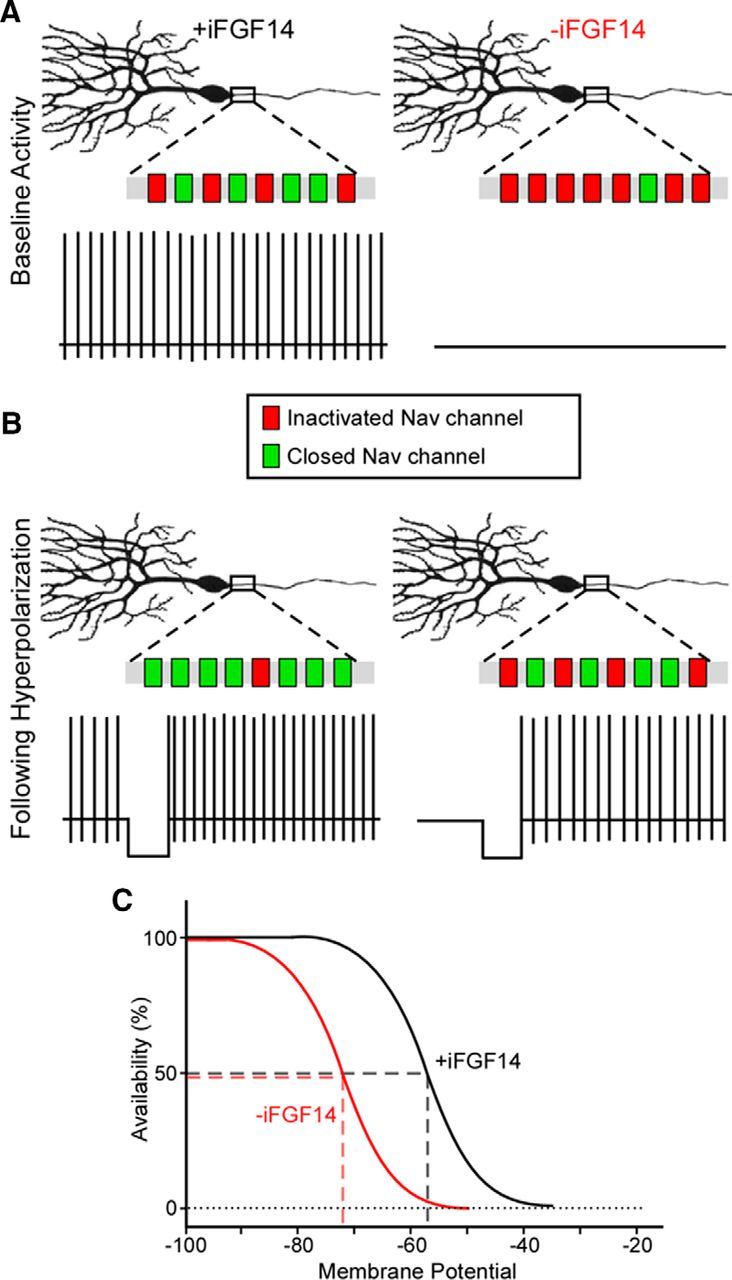
Schematic illustration of the modulatory effect of iFGF14 on Nav channel availability and repetitive firing in Purkinje neurons. A, Nav channel availability at rest is high in WT Purkinje neurons, which express iFGF14, and low in iFGF14 deficient Purkinje neurons. In addition, WT Purkinje neurons are spontaneously active, whereas most iFGF14-deficient Purkinje neurons are quiescent. B, Hyperpolarization of the membrane potential increases Nav channel availability in both WT and iFGF14-deficient Purkinje neurons and, importantly, “rescues” repetitive firing in the iFGF14-deficient cells. The total numbers of Nav channels are unchanged; only the numbers of closed channels that are available to open are affected by the membrane hyperpolarization. In addition, the availability of Nav channels is similar in iFGF14-deficient Purkinje neurons at hyperpolarized membrane potentials and in control Purkinje neurons at rest. C, In the presence of iFGF14, Nav channel availability in Purkinje neurons is shifted markedly to the right (depolarized).
