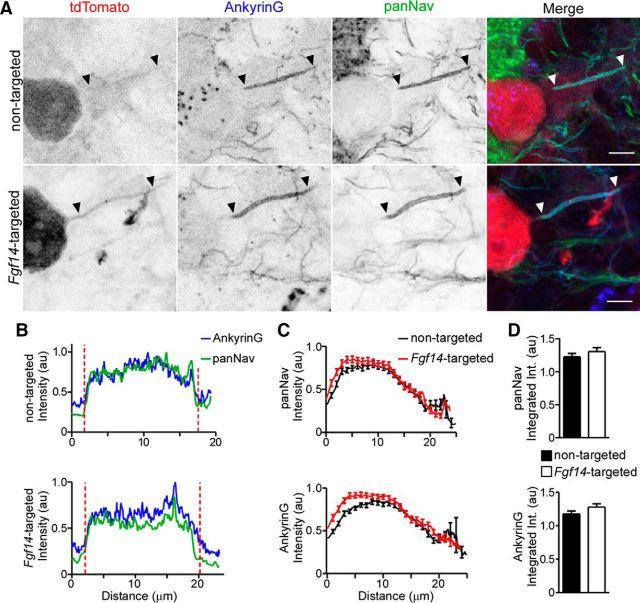
Figure 5.
Anti-Nav α-subunit immunofluorescence intensity and localization at Purkinje neuron AIS are unaffected by Fgf14-targeted shRNA. After injections of the nontargeted (top) or the Fgf14-targeted (bottom) shRNA AAV1, parasagittal sections were cut and stained with anti-Ankyrin G (blue) and anti-panNav α-subunit- (green) specific antibodies. A, Representative images of nontargeted and Fgf14-targeted shRNA-transduced Purkinje neurons, identified by tdTomato fluorescence (red); in each panel, arrowheads indicate AIS regions and scale bars are 5 μm. B, Representative line scans of anti-Ankyrin G and anti-panNav immunofluorescence intensities along the AIS of a nontargeted (top) and an Fgf14-targeted (bottom) shRNA-transduced Purkinje neuron. Vertical (red) dotted lines indicate the starts and ends of the AIS. C, Mean ± SEM immunofluorescence intensities of anti-pan Nav (top) and anti-Ankyrin G (bottom) along the AIS of Purkinje neurons transduced with either the nontargeted (n = 51 AIS, 2 animals) or the Fgf14-targeted (n = 60 AIS, 2 animals) shRNA. D, Mean ± SEM integrated immunofluorescence intensity of anti-panNav (top) and anti-Ankyrin G (bottom) staining along the AIS of Purkinje neurons transduced with the nontargeted (n = 51 AIS, 2 animals) or the Fgf14-targeted (n = 60 AIS, 2 animals) shRNA. Mean ± SEM anti-Ankyrin G and anti-Nav α-subunit labeling intensities are indistinguishable (Student's t test) in adult Purkinje neurons transduced with the nontargeted and the Fgf14-targeted shRNAs.