Fig. 1.
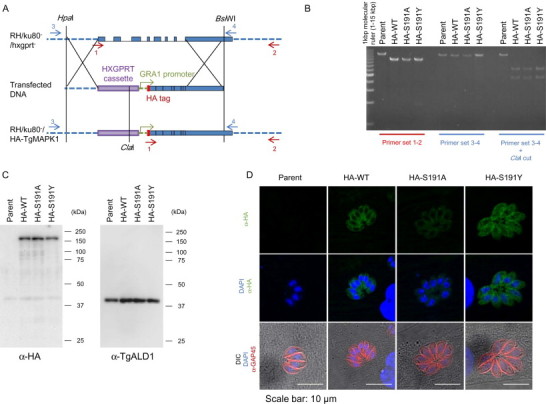
Double homologous recombination of the native TgMAPKL-1 locus in the chromosome to substitute the gatekeeper residue. (A) Schematic depiction of the knock-in construct. The red arrows show the locations of primers 1 and 2 for the PCR analysis. The blue arrows show the locations of primers 3 and 4 for the PCR-RFLP analysis. The graph shows chromosome XI around the TgMAPKL-1 locus. The blue boxes show the coding sequence of TgMAPKL-1. (B) PCR analysis of the recombinant chromosomal sequence in the knock-in clones. The 3'UTR and the coding sequence of TgMAPKL-1 were amplified with primer sets 1 and 2. The 5'UTR and the coding sequence of TgMAPKL-1 were amplified with primer sets 3 and 4. For the PCR-RFLP analysis, the PCR fragments amplified with primers 3 and 4 were digested with the ClaI restriction enzyme. Parent indicates the RH/ku80-/hxgprt- strain. (C) An anti-HA tag antibody (left panel) or an anti-TgALD1 antibody (right) was used to detect protein from the total lysate of each parasite clone. Purified parasites were lysed in 1 × SDS-PAGE sample buffer and 106 parasites/lane were loaded onto the gel. Molecular masses are shown to the right of each panel. (D) Tachyzoites of each clone were cultured in HFF cells on cover slips. Green shows the HA-tagged TgMAPKL-1 detected with the anti-HA antibody and blue shows the nuclei. To observe the parasite shape, TgGAP45 was stained and is shown in red. Scale bars = 10 µm.
