Fig. 10.
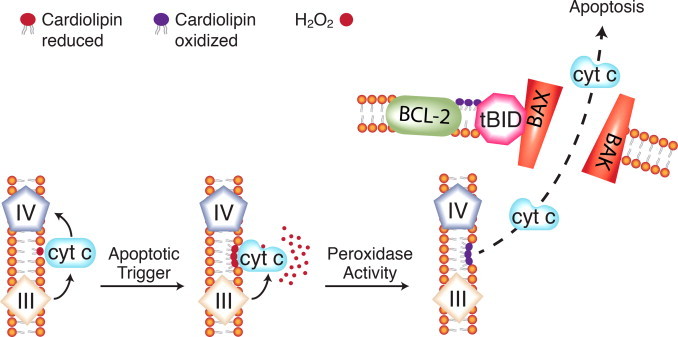
Cardiolipin oxidation and cytochrome c release in the mitochondrial pathway to apoptosis. A second, complementary model for redox signaling for apoptosis involves cytochrome c and the mitochondrial-specific phospholipid cardiolipin. Under normal conditions, cytochrome c binds cardiolipin through loose, electrostatic interactions. In the presence of hydrogen peroxide, a tighter interaction develops. This partially unfolds the cytochrome c and converts it to a peroxidase with cardiolipin as the substrate. Oxidized cardiolipin has a reduced affinity for cytochrome c, which then becomes soluble in the intermembrane space. Mitochondrial membrane lipids are reorganized during apoptosis. Oxidized cardiolipin appears in the outer mitochondrial membrane and attracts the pro-apoptotic protein tBID, thus facilitating release of cytochrome c and other apoptotic proteins from the mitochondrial intermembrane space.
