Abstract
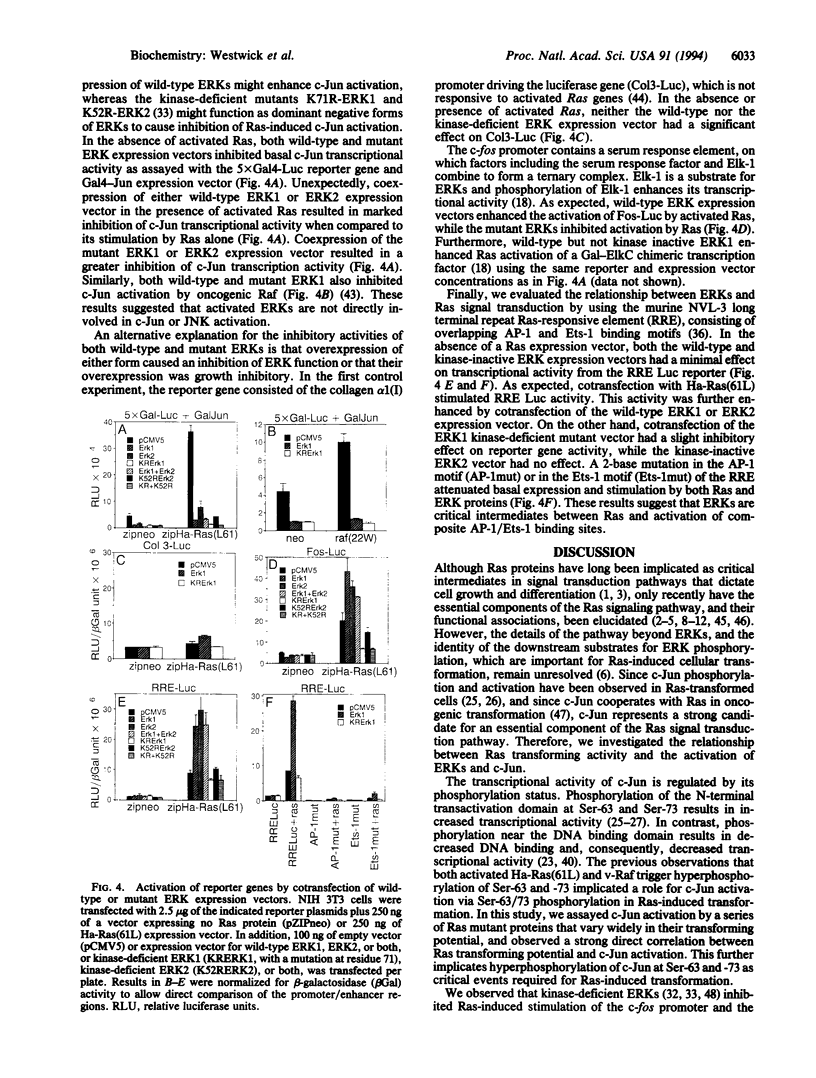
c-Jun transcriptional activity is augmented by expression of oncogenic Ras and Raf proteins. This study demonstrates a direct correlation between Ras transforming activity and c-Jun activation, supporting an important role for c-Jun in transformation by Ras. Since we observed that Ras activated c-Jun transcriptional activity by increasing phosphorylation of the c-Jun activation domain at residues Ser-63/Ser-73 and that oncogenic Ras proteins activated extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases (ERK1 and ERK2) (also known as mitogen-activated protein kinases), we evaluated the possibility that ERKs were directly responsible for c-Jun activation. Coexpression of wild-type ERKs with oncogenic Ras proteins potentiated, while kinase-defective ERKs inhibited, Ras-induced transcriptional activation from the Ras-responsive element (Ets-1/AP-1) present in the NVL-3 enhancer and the serum-response element in the c-fos promoter. In contrast, coexpression of either wild-type or kinase-defective ERKs inhibited Ras and Raf activation of c-Jun transcriptional activity. Thus, although activation of both ERK and c-Jun are downstream consequences of activation of the Ras signal transduction pathway, our results suggest that Ras-induced c-Jun phosphorylation and transcriptional activation are not a direct consequence of ERK1 and ERK2 activation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alani R., Brown P., Binétruy B., Dosaka H., Rosenberg R. K., Angel P., Karin M., Birrer M. J. The transactivating domain of the c-Jun proto-oncoprotein is required for cotransformation of rat embryo cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6286–6295. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez E., Northwood I. C., Gonzalez F. A., Latour D. A., Seth A., Abate C., Curran T., Davis R. J. Pro-Leu-Ser/Thr-Pro is a consensus primary sequence for substrate protein phosphorylation. Characterization of the phosphorylation of c-myc and c-jun proteins by an epidermal growth factor receptor threonine 669 protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15277–15285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binétruy B., Smeal T., Karin M. Ha-Ras augments c-Jun activity and stimulates phosphorylation of its activation domain. Nature. 1991 May 9;351(6322):122–127. doi: 10.1038/351122a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blenis J. Signal transduction via the MAP kinases: proceed at your own RSK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5889–5892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguski M. S., McCormick F. Proteins regulating Ras and its relatives. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):643–654. doi: 10.1038/366643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):125–132. doi: 10.1038/348125a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Smeal T., Defize L. H., Angel P., Woodgett J. R., Karin M., Hunter T. Activation of protein kinase C decreases phosphorylation of c-Jun at sites that negatively regulate its DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90241-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Solski P. A., Schaeffer J. P., MacDonald M. J., Der C. J. Activation of the cellular proto-oncogene product p21Ras by addition of a myristylation signal. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1600–1603. doi: 10.1126/science.2648572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou S. Y., Baichwal V., Ferrell J. E., Jr Inhibition of c-Jun DNA binding by mitogen-activated protein kinase. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Oct;3(10):1117–1130. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.10.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Erikson R. L. Extracellular signals and reversible protein phosphorylation: what to Mek of it all. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90411-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J. The mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14553–14556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferns M. J., Hall Z. W. How many agrins does it take to make a synapse? Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90525-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallego C., Gupta S. K., Heasley L. E., Qian N. X., Johnson G. L. Mitogen-activated protein kinase activation resulting from selective oncogene expression in NIH 3T3 and rat 1a cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7355–7359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger-Schnarr M., Benusiglio E., Schnarr M., Sassone-Corsi P. Transformation and transactivation suppressor activity of the c-Jun leucine zipper fused to a bacterial repressor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4236–4239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibi M., Lin A., Smeal T., Minden A., Karin M. Identification of an oncoprotein- and UV-responsive protein kinase that binds and potentiates the c-Jun activation domain. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2135–2148. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. S., Marais R., John S., Wynne J., Dalton S., Treisman R. Functional analysis of a growth factor-responsive transcription factor complex. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):395–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90238-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khosravi-Far R., Der C. J. The Ras signal transduction pathway. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1994 Mar;13(1):67–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00690419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolch W., Heidecker G., Lloyd P., Rapp U. R. Raf-1 protein kinase is required for growth of induced NIH/3T3 cells. Nature. 1991 Jan 31;349(6308):426–428. doi: 10.1038/349426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. J., Bortner D. M., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J., Ostrowski M. C. Mitogenic signaling by colony-stimulating factor 1 and ras is suppressed by the ets-2 DNA-binding domain and restored by myc overexpression. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5355–5362. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd A., Yancheva N., Wasylyk B. Transformation suppressor activity of a Jun transcription factor lacking its activation domain. Nature. 1991 Aug 15;352(6336):635–638. doi: 10.1038/352635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo K. X., Hurley T. R., Sefton B. M. Cyanogen bromide cleavage and proteolytic peptide mapping of proteins immobilized to membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:149–152. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01014-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marais R., Wynne J., Treisman R. The SRF accessory protein Elk-1 contains a growth factor-regulated transcriptional activation domain. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):381–393. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90237-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F. Signal transduction. How receptors turn Ras on. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):15–16. doi: 10.1038/363015a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moodie S. A., Willumsen B. M., Weber M. J., Wolfman A. Complexes of Ras.GTP with Raf-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. Science. 1993 Jun 11;260(5114):1658–1661. doi: 10.1126/science.8503013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nehls M. C., Rippe R. A., Veloz L., Brenner D. A. Transcription factors nuclear factor I and Sp1 interact with the murine collagen alpha 1 (I) promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4065–4073. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owaki H., Makar R., Boulton T. G., Cobb M. H., Geppert T. D. Extracellular signal-regulated kinases in T cells: characterization of human ERK1 and ERK2 cDNAs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Feb 14;182(3):1416–1422. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91891-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagès G., Lenormand P., L'Allemain G., Chambard J. C., Meloche S., Pouysségur J. Mitogen-activated protein kinases p42mapk and p44mapk are required for fibroblast proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8319–8323. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Hughes K., Franklin C. C., Kraft A. S., Leevers S. J., Woodgett J. R. Co-purification of mitogen-activated protein kinases with phorbol ester-induced c-Jun kinase activity in U937 leukaemic cells. Oncogene. 1993 Feb;8(2):407–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy M. A., Langer S. J., Colman M. S., Ostrowski M. C. An enhancer element responsive to ras and fms signaling pathways is composed of two distinct nuclear factor binding sites. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Jul;6(7):1051–1060. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.7.1324418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rippe R. A., Brenner D. A., Leffert H. L. DNA-mediated gene transfer into adult rat hepatocytes in primary culture. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):689–695. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins D. J., Zhen E., Owaki H., Vanderbilt C. A., Ebert D., Geppert T. D., Cobb M. H. Regulation and properties of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1 and 2 in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):5097–5106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels M. L., Weber M. J., Bishop J. M., McMahon M. Conditional transformation of cells and rapid activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade by an estradiol-dependent human raf-1 protein kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6241–6252. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Der C. J., Verma I. M. ras-induced neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells: possible involvement of fos and jun. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3174–3183. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh T., Nakafuku M., Kaziro Y. Function of Ras as a molecular switch in signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24149–24152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth A., Alvarez E., Gupta S., Davis R. J. A phosphorylation site located in the NH2-terminal domain of c-Myc increases transactivation of gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23521–23524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth A., Gonzalez F. A., Gupta S., Raden D. L., Davis R. J. Signal transduction within the nucleus by mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24796–24804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack J. L., Parker M. I., Robinson V. R., Bornstein P. Regulation of collagen I gene expression by ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4714–4723. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeal T., Binetruy B., Mercola D. A., Birrer M., Karin M. Oncogenic and transcriptional cooperation with Ha-Ras requires phosphorylation of c-Jun on serines 63 and 73. Nature. 1991 Dec 12;354(6353):494–496. doi: 10.1038/354494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeal T., Binetruy B., Mercola D., Grover-Bardwick A., Heidecker G., Rapp U. R., Karin M. Oncoprotein-mediated signalling cascade stimulates c-Jun activity by phosphorylation of serines 63 and 73. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3507–3513. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton V. P., Jr, Nichols D. W., Laudano A. P., Cooper G. M. Definition of the human raf amino-terminal regulatory region by deletion mutagenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):639–647. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Aelst L., Barr M., Marcus S., Polverino A., Wigler M. Complex formation between RAS and RAF and other protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6213–6217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtek A. B., Hollenberg S. M., Cooper J. A. Mammalian Ras interacts directly with the serine/threonine kinase Raf. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90307-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warne P. H., Viciana P. R., Downward J. Direct interaction of Ras and the amino-terminal region of Raf-1 in vitro. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):352–355. doi: 10.1038/364352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. F., Settleman J., Kyriakis J. M., Takeuchi-Suzuki E., Elledge S. J., Marshall M. S., Bruder J. T., Rapp U. R., Avruch J. Normal and oncogenic p21ras proteins bind to the amino-terminal regulatory domain of c-Raf-1. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):308–313. doi: 10.1038/364308a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]