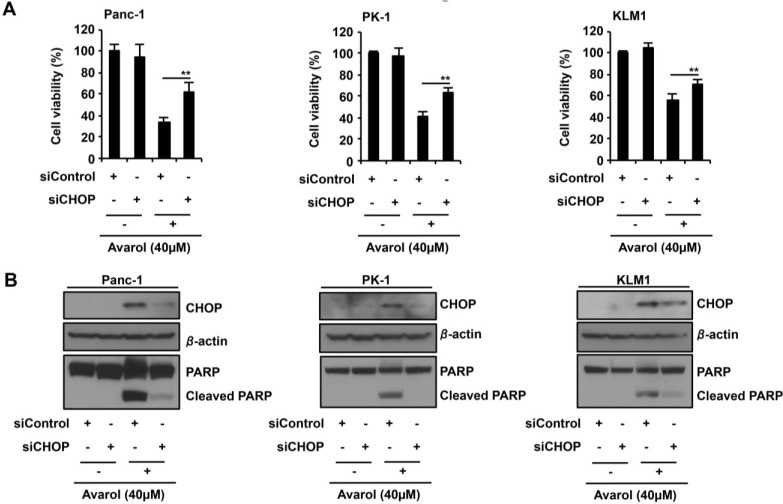
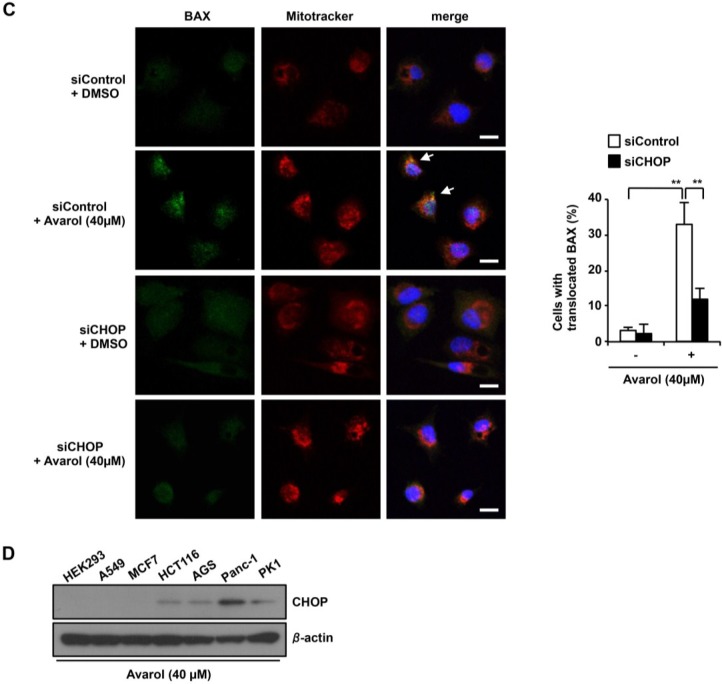
Figure 4.
ER stress response-induced CHOP plays a key role in avarol-induced apoptosis. (A,B) CHOP knockdown suppresses avarol-induced apoptosis; Panc-1, PK1, and KLM1 cells were manipulated with siControl or siCHOP for 24 h and were then treated with 40-μM avarol for 18 h. (A) Cell viability was determined using MTT assays. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three simultaneously performed experiments; (B) Whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Blots were cut based on protein sizes; (C) The effect of CHOP knockdown on Bax translocation to mitochondria upon avarol treatment. Using the same procedure described in (A,B), endogenous active Bax was visualized using an anti-Bax antibody (N-20) and confocal microscopy. MitoTracker (red) was used as a mitochondria-specific marker. Merged images are shown, and the yellow color (white arrow) represents co-localization of Bax (green) and MitoTraker (red; scale bar, 20 μm). Percentage BAX translocation was determined by counting three different fields (20–40 cells/field). Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three different experiments. P values were calculated using two-way ANOVA; ** P < 0.01 (A,C); (D) Avarol induces CHOP expression in Panc-1 and PK1 cells. HEK293, A549, MCF7, HCT116, AGS, Panc-1, and PK1 cells were treated with 40 μM avarol for 24 h, and whole-cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Blots were excised based on protein sizes.