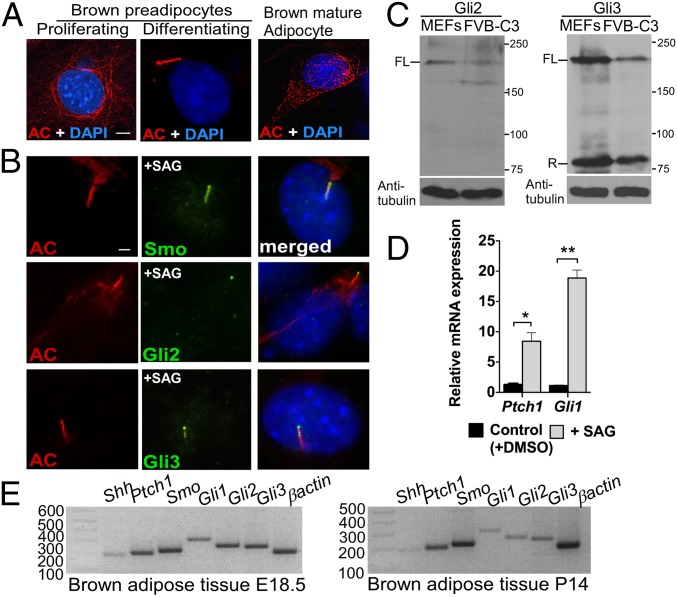
Fig. 1.
BAT possesses major Hh-pathway components. (A) Immunofluorescence with antibodies against acetylated tubulin (AC; red), a marker for both cytoplasmic microtubules and primary cilium, was performed in proliferating and differentiating brown preadipocytes and in mature brown adipocytes generated from the FVB-C3 cell line (n = 3). Staining of the cytoplasmic tubulin network is seen in cells lacking primary cilia, but acetylated tubulin relocalized to the cilium upon assembly, resulting in intense rod-shaped staining. (Scale bar: 5 μm.) (B) Double immunofluorescence staining with antibodies against acetylated tubulin (red) and Hh-pathway components Smo, Gli2, and Gli3 (green) in FVB-C3 cells. (Scale bar: 10 μm.) (C) Western blot analysis of Gli2 and Gli3 protein abundance in WT embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and FVB-C3 cells. α-Tubulin was used as a loading control. FL, full length; R, repressor. (D) qRT-PCR analysis of Ptch1 and Gli1 in FVB-C3 cells treated with SAG relative to untreated control cells (n = 3). Data are presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. (E) RT-PCR of Shh, Ptch1, Smo, Gli1, Gli2, and Gli3 in BAT isolated from E18.5 WT embryos and 14-d-old pups (P14) (n = 4).