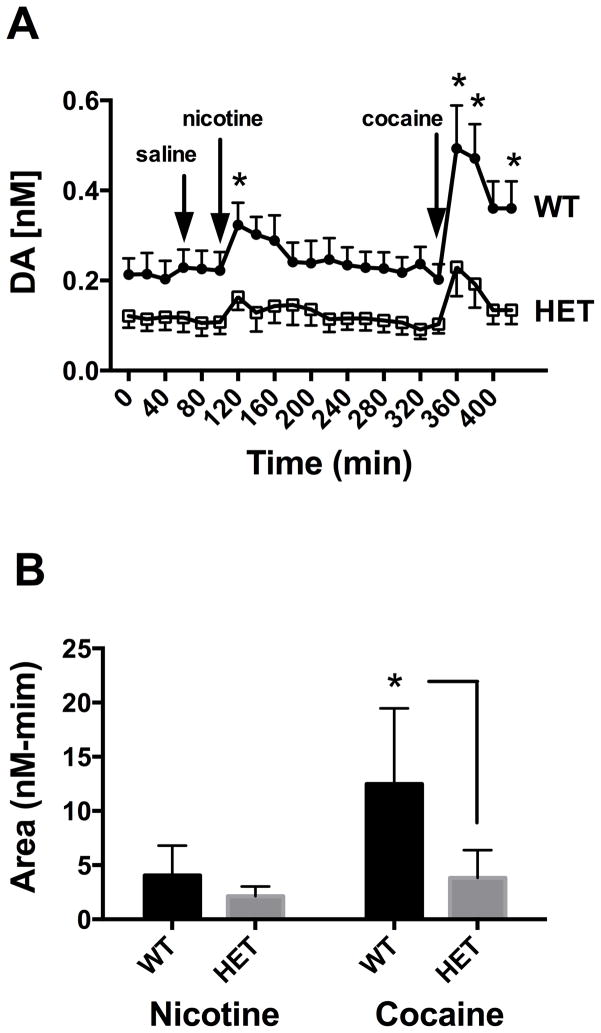
Figure 1.
Evaluation of the impact of CHT heterozygosity on basal and drug-evoked elevations in extracellular DA. A) Basal and drug evoked DA levels as measured by microdialysis. Each animal was exposed to saline, nicotine (1mg/kg) and cocaine (10 mg/kg) as designated by the arrows. Data reflects mean +/− SEM from n=9 animals of each genotype. # = significant genotype effect as assessed by a Repeated Measures two-way ANOVA analysis (P<0.05). * = significant genotype differences in DA elevations induced by drug injection over baseline, assessed by Bonferroni post-hoc analysis of time-matched samples (P<0.05). B) Cumulative response to nicotine and cocaine by genotype. Area under the curve (AUC) analysis of data presented in A) was performed for the nicotinic and cocaine responses of each genotypes post injection. Peaks were detected automatically In Prism software. Data were analyzed via two-way ANOVA. Significant genotype, drug and interaction effects were detected (P<.05). Uncorrected Fisher’s LSD post-hoc comparisons between genotypes for each drug condition revealed a non-significant genotype effect for cocaine and a significant (*P=.0002) genotype effect for cocaine.