Figure 4. Activation of Slit2/Robo1 signaling led to an activation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
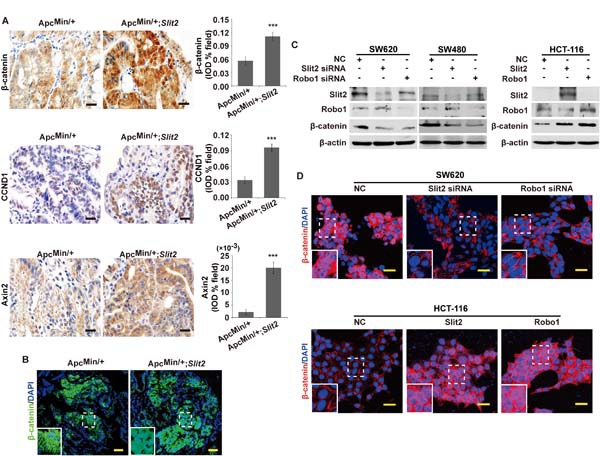
Expression of β-catenin, CCND1 and Axin2 in the tumor tissues of ApcMin/+ and ApcMin/+;Slit2 mice was examined by IHC, and the results were quantitatively determined using IPP software and expressed as the mean ± S.D. (A). The subcellular location of β-catenin was examined in the tumor tissues of ApcMin/+ and ApcMin/+;Slit2 mice by IF (B). Inactivation of Slit2/Robo1 signaling by suppressing Slit2 or Robo1 expression inhibits the expression of β-catenin in SW620 and SW480 cells, but conversely, activation of Slit2/Robo1 signaling through overexpressing Slit2 or Robo1 expression promotes β-catenin expression in HCT-116 cells (C). Inactivation of Slit2/Robo1 signaling by siRNA against Slit2 or Robo1 suppresses nuclear translocation of β-catenin in SW620 cells, and overexpression of Slit2 or Robo1 promotes nuclear translocation of β-catenin in HCT-116 cells (D). All results represent at least three separate experiments (C and D). The IHC and IF staining of the mouse tissues are representative of 11 mice per group (All mice were 24-week-old). The results of IHC were determined using IPP software, and expressed as the mean ± S.D. *: P < 0.05, ***: P < 0.001. Scale bars, 20 μm (A) and 25 μm (B and D).
