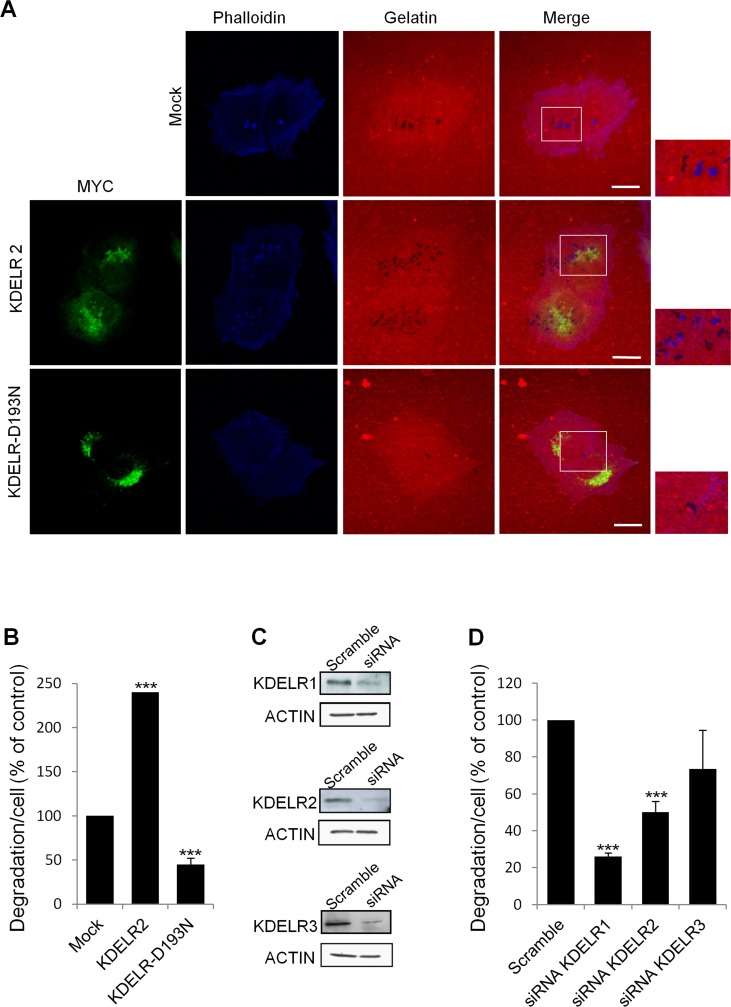
Figure 4. KDELR inhibition impairs degradation of the ECM.
(A) A375MM cells were transfected with empty vector (Mock), KDELR2-myc or KDELR-D193N-myc (as indicated) for 24 h, and grown on rhodamine-conjugated crosslinked gelatine (red) for 16 h in the presence of BB94. Following BB94 wash-out, the cells were incubated for a further 3 h and then fixed and stained with -phalloidin (blue, Mock) and an anti-myc antibody (green, KDELR2-myc and KDELR-D193N-myc). Merged images of red and blue (Mock) and red, blue and green signals (KDER2 and KDELR-D193NL) are also shown. Invadopodia are shown in the enlargements of the boxed regions (small right panels: blue and red signals). Scale bars, 10 μm. The images are representative of at least four independent experiments. (B) Quantification of the degradation area per cell. Data are degradation area per cell (% of control), as means ±SEM of four independent experiments, with at least 100 cells quantified per experiment. ***p <0.001, compared to Mock cells (t-test). (C) A375MM cells were treated without (Scramble) or with siRNAs targeting KDELR1, KDELR2 and KDELR3 (siRNA KDELR) for 96 h. KDELR1, KDELR2, and KDELR3 expression levels were assessed by Western blotting, using a pan anti-KDELR antibody, an antibodies specifically directed against KDELR2 and KDELR3, respectively. Actin was used as loading control. (D) A375MM cells were treated as in C, and then 72-h post interference they were plated for 24 h on rhodamine-conjugated gelatine in the presence of BB94. Following the BB94wash-out, the cells were incubated for a further 3 h, then fixed and scored for their ability to degrade the ECM. Data are degradation area per cell (% of control), as means ±SEM from three independent experiments, with at least 100 cells quantified per experiment. ***p <0.001, compared to Scrambled cells (t-test).