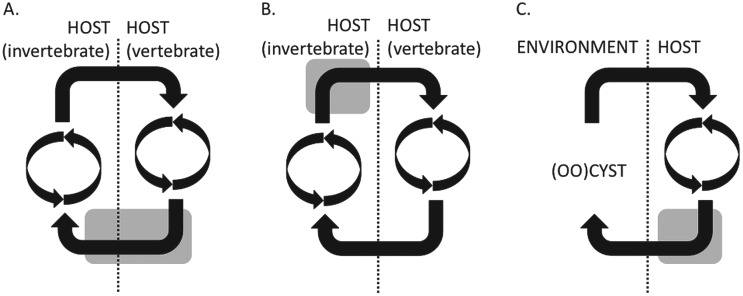
Fig. 1.
Simplified schematic representations of the life cycles of vector- and fecal–oral-transmitted parasites. (A) The Plasmodium falciparum life cycle, which has two cycles of asexual growth, one in each host, and the sexual stages (grey shading) which span transmission from one host to another; (B) the T. brucei life cycle, in which the sexual stages appear to take place in the insect host, after a cycle of asexual cell divisions but before transmission to the mammalian host; (C) the Cryptosporidium and Eimeria life cycle, in which the sexual stages all take place within the single host and cysts are passed into the environment.