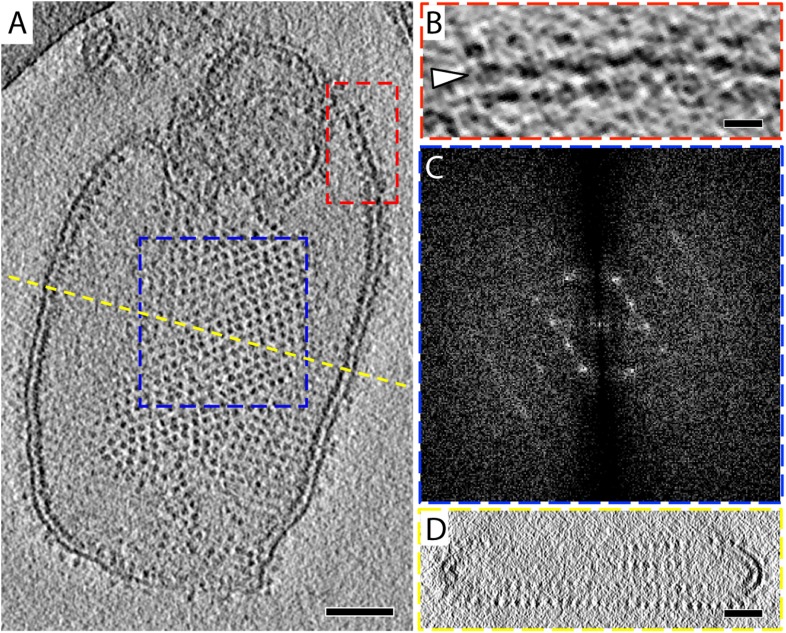
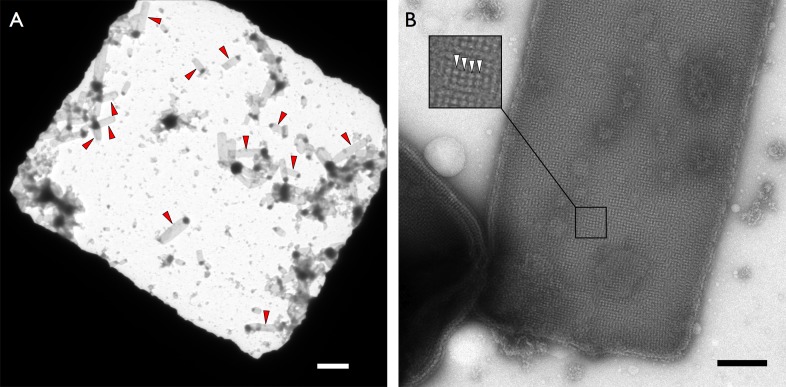
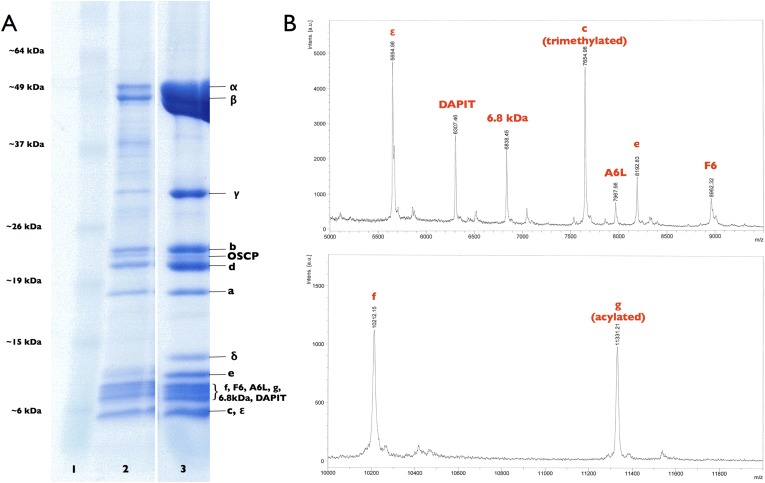
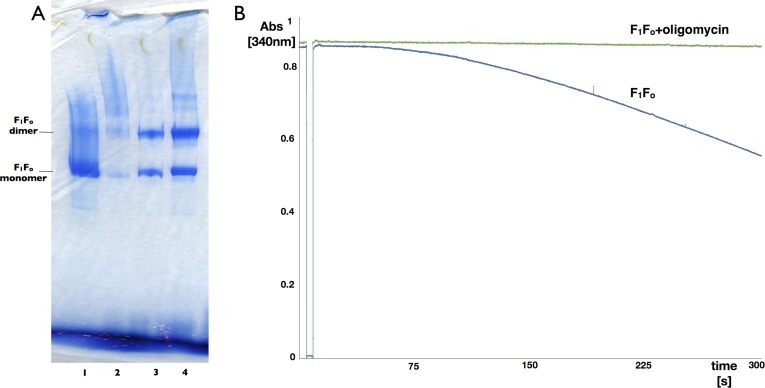
(A) BN polyacrylamide gradient gel (4–12%) of purified F1Fo ATP synthase solubilized in decylmaltoside (lane 1 and 2, 15 μg and 2 μg respectively) and of digitonin-resolubilised 2D crystals (lane 3 and 4, 30 μg and 90 μg respectively). Bands of lower molecular weight subcomplexes, that is, Fo or c8, are weak or absent. The dimer band in lane 1 and 2 presumably stems from mitochondrial F1Fo ATP synthase dimers preserved by mild purification conditions. The dimer band visible in lane 3 and 4 most likely represents non-physiological F1Fo ATP synthase dimers that form in the 2D crystals. (B) Typical ATPase activity and oligomycin-sensitivity of digitonin-resolubilised F1Fo ATP synthase isolated from 2D crystals. The hydrolysis of ATP by the F1Fo ATP synthase was monitored using an enzyme couple assay by detecting NADH oxidation at 340 nm at 20°C in the absence (blue) or presence (green) of oligomycin. Oligomycin inhibits ATP hydrolysis through F1 by stopping rotation of the Fo motor, that is, oligomycin sensitivity gives a measure of the amount of coupled, intact F1Fo ATP synthase complexes in the preparation, in this case >95%.