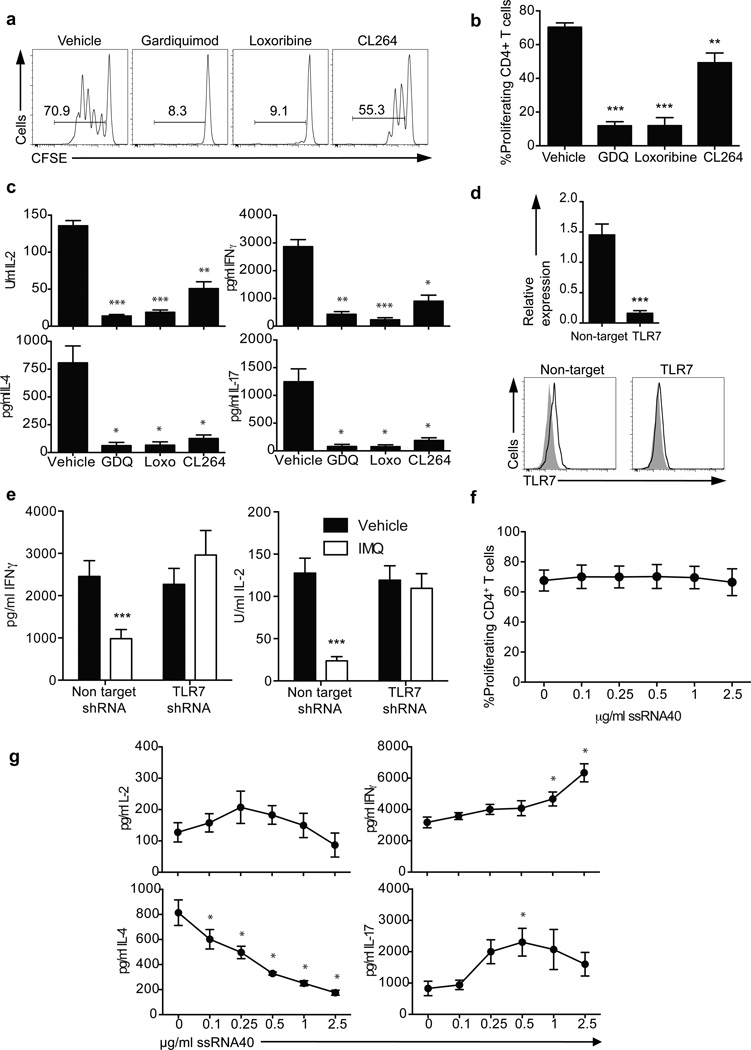
Figure 2.
The inhibitory effect of IMQ is TLR7-specific. CD4+ T cells were stimulated for 3 days in the presence of the TLR7 agonists GDQ, Loxoribine and CL264. a. Histograms show CFSE-labeled CD4+ T cell proliferation 3 days after stimulation. Numbers in histograms represent the frequency of viable proliferating CD4+ T cells. b. Frequency of viable proliferating CD4+ T cells. c. Cytokine secretion measured by ELISA after 3 days. d. CD4+ T cells were stimulated in the presence of a shRNA specific for TLR7 (clone TRCN0000056973) or a non-target control. Transduced cells were sorted based on GFP expression at day 5 and TLR7 RNA (upper) and protein (lower) expression were examined. Histograms represent isotype control (gray histograms) and TLR7 (open histograms). e. Non-target and TLR7 shRNA-transduced CD4+ T cells were stimulated in the presence (white bars) or absence (black bars) of IMQ for 3 days and IL-2 and IFN-γ secretion was measured by ELISA. f. CFSE-labeled CD4+ T cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 in the presence of different doses of ssRNA40. Statistical analysis of the frequency of proliferating CD4+ T cells with increasing concentrations of ssRNA40 (n=4 donors in 4 independent experiments). g. IL-2, IFN-γ, IL-4 and IL-17 secretion measured at day 3 after activation by ELISA (n=4 donors in 4 independent experiments). Statistical analysis represents mean±s.e.m. of seven independent experiments performed for a, b, d and e, five experiments for c and four experiments for f and g. * p<0.05, ** p<0.005, *** p<0.0005.