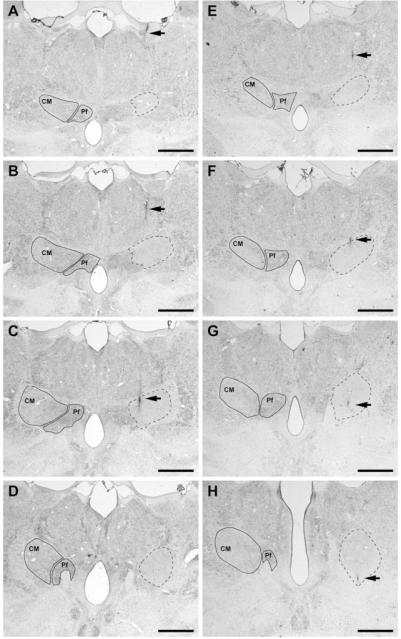
FIG. 2.
Coronal sections through the primate thalamus (Nissl-stained) showing the extent and location of the lesioned area obtained after delivering 0.1 μL of kainic acid. (A–H) Coronal sections through four representative levels of either the primate thalamus no. 41 (A–D) or the primate no. 44 (E–H) comprising the full rostrocaudal extent of the CM nucleus (A–D as well as E–H from rostral to caudal). Within each section, the boundaries of the CM and the parafascicular nucleus (Pf) are delineated in the contralateral thalamus for reference purposes. On the left thalamus (shown on the right side of each microphotograph), the location and extent of the lesion is delineated by dashed lines. It could be easily appreciated that the kainate-induced lesion comprises the full extent of the nucleus, neighboring nuclei remaining largely unaffected. Arrows illustrate the needle track. Scale bar A–H: 2,500 μm.