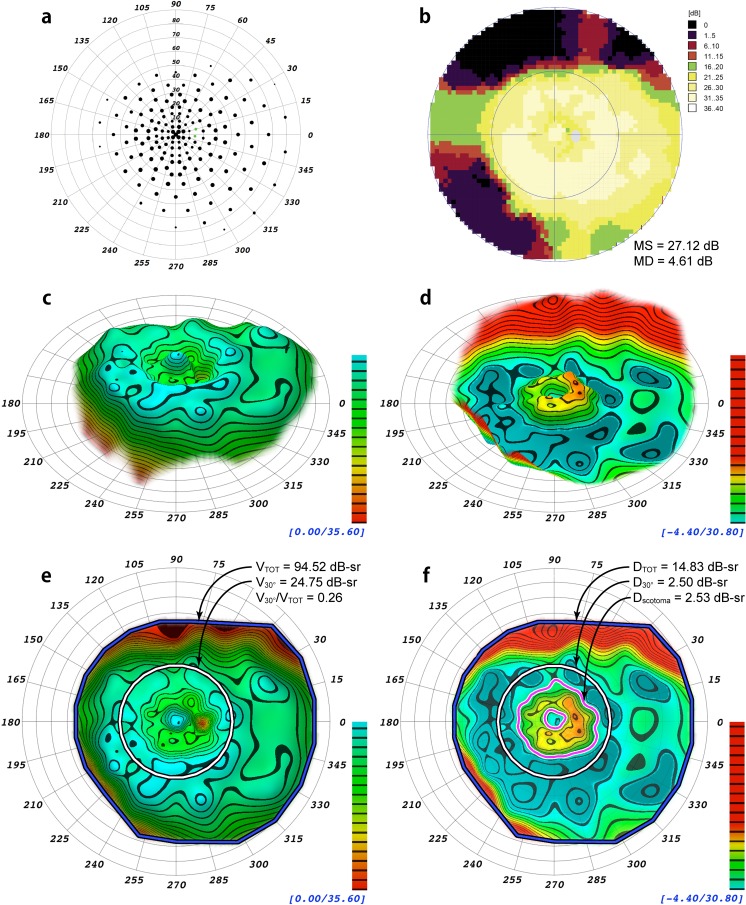
Figure 3.
Comparison from a patient with autosomal dominant pericentral retinitis pigmentosa in association with a reported heterozygous mutation in NR2E3,27 NM_014,249.2: c.166G>A(P.G56R), and a second heterozygous variation, NM_005,802.3:c.2643C>G(P.H881Q), of unknown significance in TOPORS.29 (a) Scaled-point plot of DLS values. (b) Incremental color-scale plot generated by the Octopus 900 (Haag-Streit). (c) Oblique topographical view generated by VFMA. (d) Defect space model generated by VFMA depicting pericentral field loss. (e) En face view with the selection boundaries for the total volume (blue/black) and the central 30° volume (white/black). (f) En face view of the defect space. The volume of the pericentral scotoma defect (the region between the magenta/white contour lines) is shown. Because of the existence of negative values (the patient had greater than normal sensitivity in some regions) between the outer boundary of the scotoma and the 30° circle, the pericentral scotoma volume is slightly larger than that of D30°.