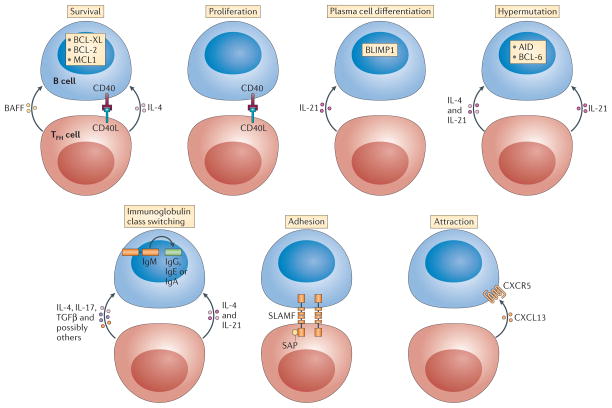
Figure 2. Categories of T cell help to B cells.
Help can come in many different forms and can have different consequences for different processes. T follicular helper (TFH) cells provide seven main forms of T cell help to B cells: signals that promote survival, proliferation, plasma cell differentiation, hypermutation, class-switch recombination, adhesion and chemoattraction (cell migration). For simplicity, only a few examples of factors that are important for each process are shown, although many more molecules are involved in the regulation of the processes. Several of these pathways are reviewed in detail elsewhere64,73,85. Some molecules have pleiotropic effects, resulting in combinatorial possibilities and functional redundancies between molecules. AID, activation-induced cytidine deaminase; BAFF, B cell-activating factor; BCL, B cell lymphoma; BLIMP1, B lymphocyte-induced maturation protein 1; CD40L, CD40 ligand; CXCL13, CXC-chemokine ligand 13; CXCR5, CXC-chemokine receptor 5; IL, interleukin; MCL1, myeloid cell leukaemia 1; SAP, SLAM-associated protein; SLAMF, signalling lymphocytic activation molecule F; TGFβ, transforming growth factor-β.