Figure 5. F4 peptide inhibits melanoma cell migration and tumor growth.
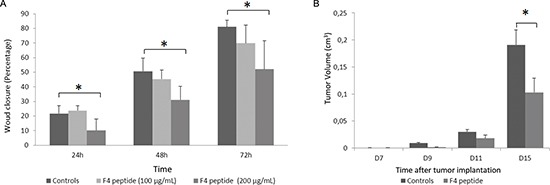
(A) Measurement of the wound closure in scratch wound assay, demonstrating that wound closure was significantly delayed when cells were incubated with F4 peptide after 24 h (−53%, p < 0.05), 48 h (−39%, p < 0.05) or 72 h (−36%, p < 0.05) of incubation. Histogram represents the mean ± sd of five experiments; *, p < 0.05, significantly different from controls (Mann and Withney non parametric U-test). (B) F4 peptide inhibits tumor growth in murine melanoma model in vivo. Tumor size was measured at days 7, 9, 11 and 15. Tumor volumes were determined according to v = 1/2 A x B2, where A denotes the largest dimension of the tumor and B represents the smallest dimension. Tumor volume was significantly lower at day 15th (−30%) in F4 peptide-injected mice vs controls. Histogram represents the mean ± sem of ten mice; *, p < 0.05, significantly different from controls (Mann and Withney non parametric U-test).
