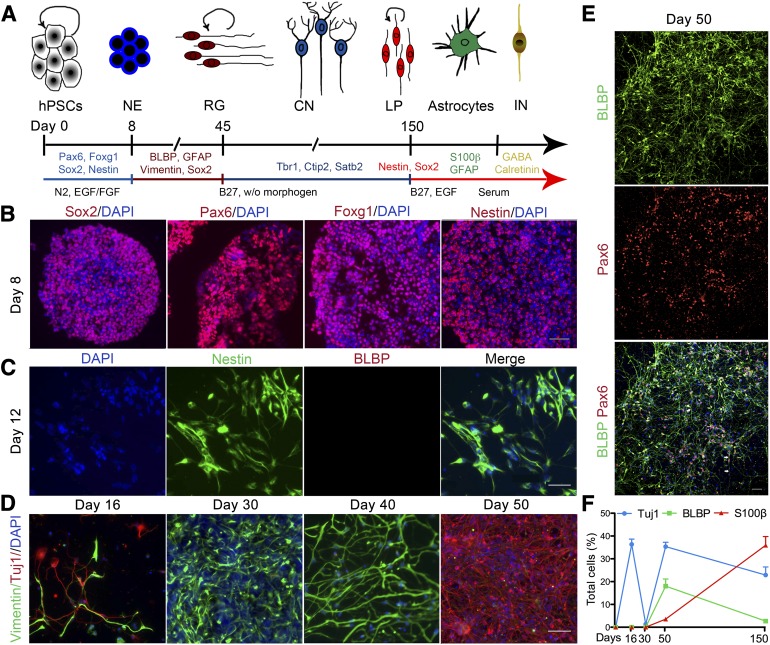
Figure 1.
Differentiation of RG from hESCs. (A): Summary of the different stages of cells in culture. hESCs were first differentiated to NE cells, followed by differentiation into RG cells without morphogens. RG continuously generated CNs until around day 150, when the RG transitioned to a LP stage that primarily generated astrocytes and some INs. (B): At day 8, early neural progenitors expressed neuroepithelial markers Sox2, Pax6, Foxg1, and nestin. Nuclei are indicated by DAPI staining. (C): Day 12 cells expressed the neuroepithelial marker nestin but were negative for the RG marker BLBP. (D): A brief wave of Tuj1-positive neurons was present before the appearance of RG and then reappeared after the generation of RG. Neural progenitors were stained with vimentin. (E): Day 50 cultures consisted of long process-bearing cells, which stained positive for BLBP and for Pax6 in the nucleus. RG typically exhibited two types of morphology, unipolar (top white arrow) or bipolar (bottom two white arrows). (F): Temporal expression of lineage markers among total cells. Data are mean ± SEM; n = 5. Scale bars = 50 μm. Abbreviations: BLBP, brain lipid-binding protein; CNs, cortical neurons; DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; EGF, epidermal growth factor; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; hESCs, human embryonic stem cells; INs, interneurons; LP, late progenitor; NE, neural epithelial; RG, radial glia; w/o, without.