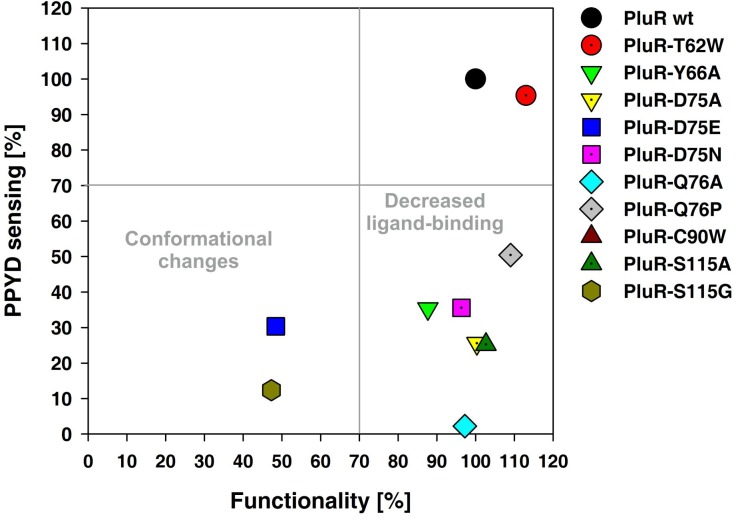
Fig 3. Amino acid replacements within the SBD of PluR caused either functionality or impaired PPYD-sensing.
The PluR derivatives D75E and S115G dramatically decreased functionality and hence decreased its ability to bind and activate pcfA P.l. promoter (lower left quadrant). Replacements within the TYDQCS-motif of PluR decreased the ability of PluR to sense PPYD. The most drastic influence on PPYD-sensing is detectable with the replacement of Y66A, D75A, D75N, Q76A, Q76P and S115A in PluR (lower right quadrant). Only the replacement T62W showed no effect and same induction levels as PluR wild type (upper right quadrant). The activity of the pcfA P.l. promoter was measured via luminescence as read-out and the depicted values were taken 2 h after addition of 0.1% (w/v) arabinose (lower axis) or 3.5 nM PPYD (left axis) and compared to PluR wild type, which values were set to 100%. To evaluate the different PluR derivatives, a cut-off of 70% was set for each value. RLU (relative light units) values for all PluR derivatives and PluR wild type are depicted in S3 Table.