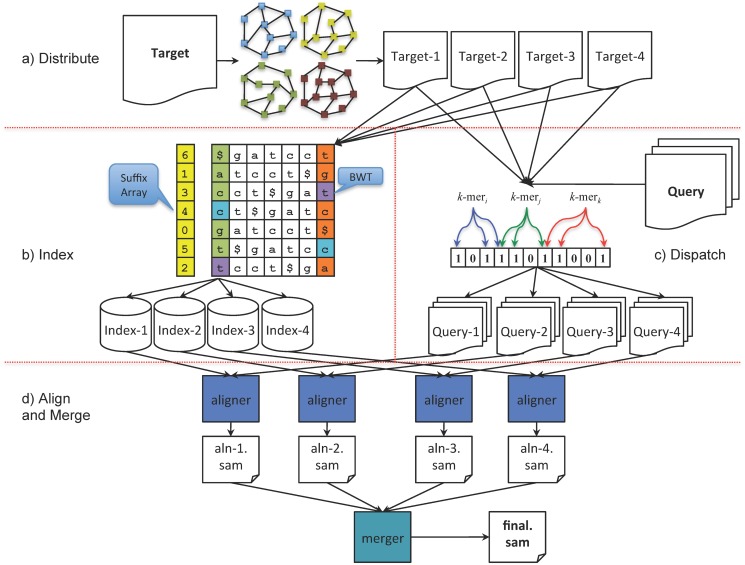
Fig 1. DIDA workflow with four partitions as an example.
(a) First, we partition the targets into four parts using a heuristic balanced cut. (b) Next, we create an index for each partition. (c) The reads are then flowed through Bloom filters to dispatch the alignment task to the corresponding node(s). (d) Finally, the reads are aligned on all four partitions and the results are combined together to create the final output.