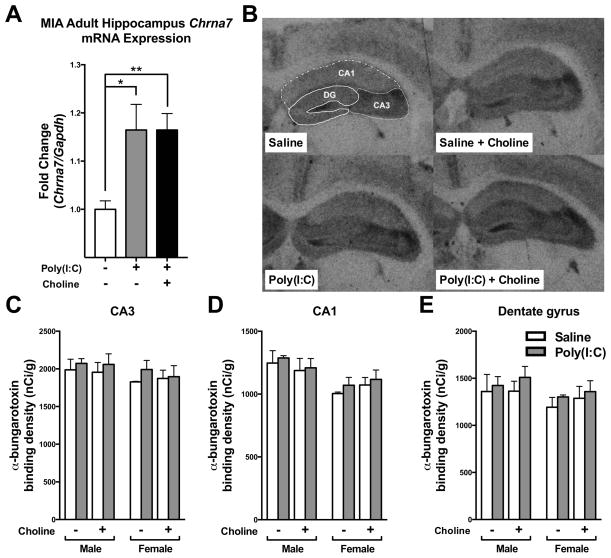
Fig. 2.
α7nAChR expression in the hippocampus of adult MIA offspring. (A) Compared to control offspring, hippocampal Chrna7 mRNA expression was higher in MIA offspring. The elevation of Chrna7 mRNA expression was not affected by maternal choline supplementation diet, however. Chrna7 mRNA expression was normalized by Gapdh. Saline n = 4; Poly(I:C) n = 12, Poly(I:C)+Choline n = 8. (B) Film images of 125Iα-bungarotoxin binding to transverse sections through the hippocampus of saline and MIA offspring given a control or choline supplementation diet. The dashed lines illustrate how the subdivisions of the hippocampus were delineated. (C–E) The density of 125Iα–bungarotoxin (α–BTX) binding to sections of hippocampal formation from saline and MIA offspring given control or choline supplementation diets. Generally, no difference was detected among the groups. Male, Saline-Control diet: n = 3 litters; Poly(I:C)-Control diet: n = 3 litters; Saline-Choline diet: n = 3 litters; Poly(I:C)-Choline diet: n = 4 litters. Female. Saline-Control diet: n = 2 litters; Poly(I:C)-Control diet: n = 4 litters; Saline-Choline diet: n = 5 litters; Poly(I:C)-Choline diet: n = 4 litters. MIA and maternal choline supplementation did not affect the density of α–BTX binding in (C) CA3, (D) CA1 and (E) dentate gyrus (DG). Chrna7: nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha 7 subunit. Data are presented as Mean ± SEM. Significant difference between groups is labeled as * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.