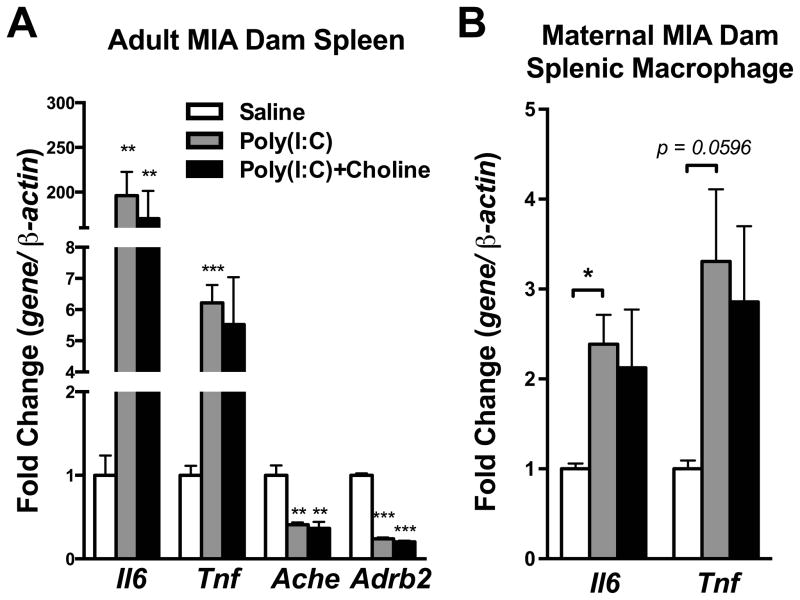
Fig. 3.
Cytokines and cholinergic signaling genes were altered in maternal spleen and splenic macrophage by maternal poly(I:C) injection, but not by maternal choline supplementation. (A) Il6 and Tnf mRNA were increased while Ache and Adrb2 were decreased in the dam’s spleen 3 hr after maternal poly(I:C) injection. Choline supplementation did not affect these changes in gene expression. Saline n = 3 dams; Poly(I:C) n = 4 dams, Poly(I:C)+Choline n = 4 dams. (B) Consistent with the results from the spleen, Il6 and Tnf mRNA were increased in macrophages after maternal poly(I:C) injection, and choline supplementation had little effect. Gene expression was normalized by β-actin. Saline n = 3; Poly(I:C) n = 4, Poly(I:C)+Choline n = 4. Ache: acetylcholinesterase, Adrb2: beta-2 adrenergic receptor, Chrna7: nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha 7 subunit, Il6: interleukin-6, Tnf: tumor necrosis factor alpha. Data are presented as Mean ± SEM. Significant difference between groups is labeled as * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.