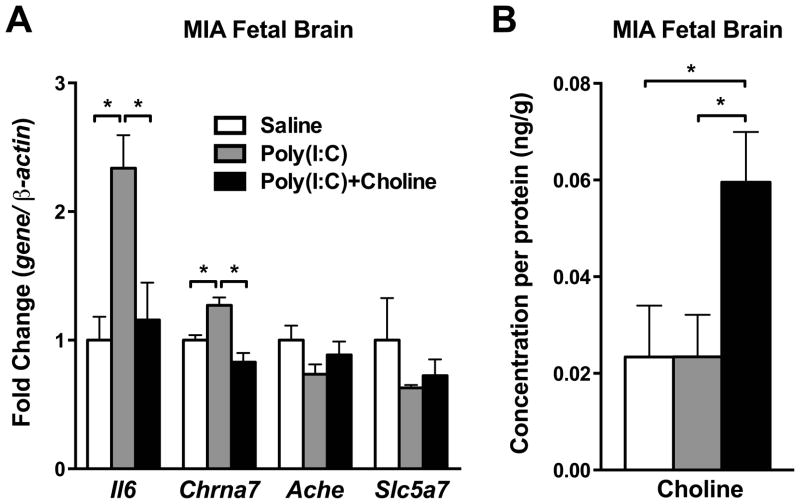
Fig. 5.
Cytokines and cholinergic signaling genes were altered in fetal brain by maternal poly(I:C) injection and maternal choline supplementation. (A) Maternal poly(I:C) injection increased Il6 and Chrna7 mRNA in fetal brain, and maternal choline supplementation prevented these increases. No changes were found in Ache and Slc5a7 among groups. Gene expression was normalized by β-actin. Saline n = 3 litters; Poly(I:C) n = 3–4 litters, Poly(I:C)+Choline n = 3–4 litters. (B) Maternal choline supplementation was associated with increased trend of choline levels in MIA fetal brain. Each n = 3 litters. Ache: acetylcholinesterase, Chrna7: nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha 7 subunit, Il6: interleukin-6, Slc5a7: choline transporter 1. Data are presented as Mean ± SEM. Significant difference between groups is labeled as * p < 0.05.