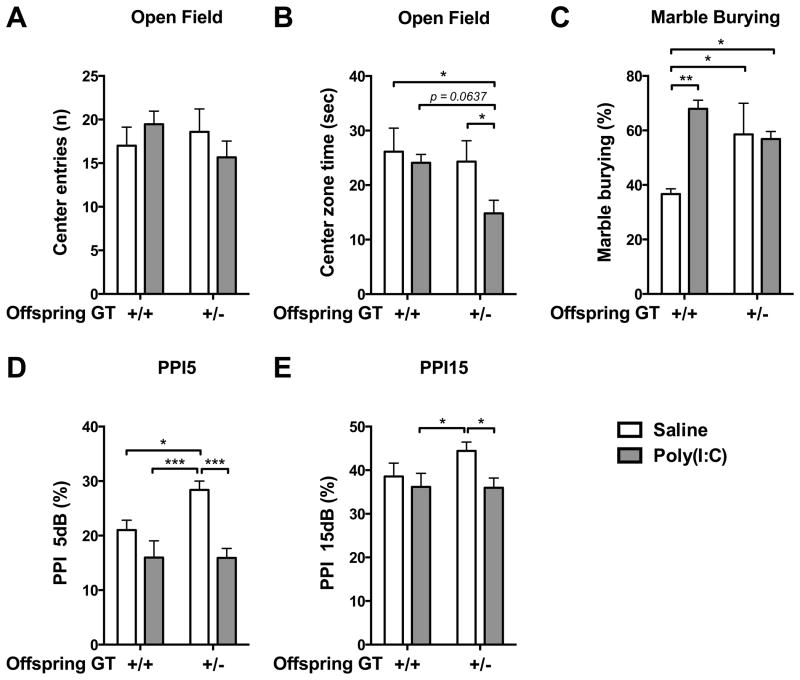
Fig. 8.
Compared to wild type, Chrna7+/− offspring were more susceptible to MIA, generally exhibiting more autistic- and schizophrenia-like behaviors. (A–B) Chrna7+/− MIA offspring displayed anxiety-like behavior in the open field, while wild-type MIA offspring did not. (C) Wild-type MIA offspring displayed more repetitive behavior in the marble burying test compared to saline offspring. The baseline of repetitive behavior in the Chrna7+/− offspring was higher than in the wild-type saline offspring and there was no effect of MIA in the Chrna7+/− offspring. (D–E) Chrna7+/− MIA offspring displayed a PPI deficit at PPI5 and PPI15, while wild-type MIA offspring exhibited normal PPI5 and PPI15. Saline: n = 4–5 litters, Poly(I:C): n = 4–6 litters. Data are presented as Mean ± SEM. Significant difference between groups is labeled as * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.