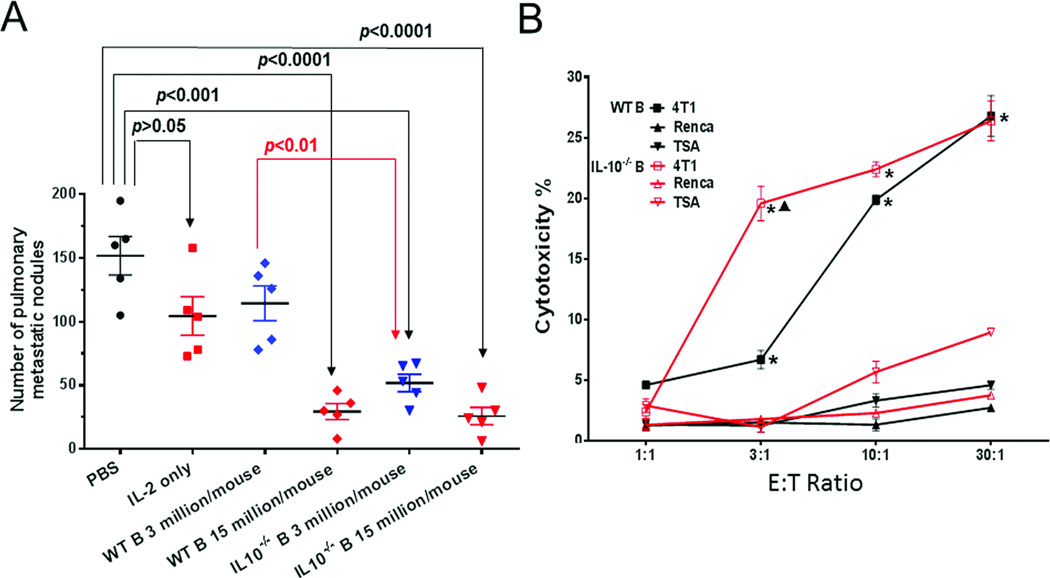
Figure 2.
IL-10−/− 4T1 TDLN B cells are more effective than WT 4T1 TDLN B cells in vitro and in vivo. (A) Number of pulmonary metastatic nodules after adoptive transfer of WT vs. IL-10−/− B cells. Groups of mice (n = 5 mice per group) received adoptively transferred B cells plus IL-2, 2 weeks after intramammary fat pad injection of 4T1 tumor cells. Control groups received PBS or IL-2. Each dot represents the number of pulmonary metastasis in a single mouse, the mean (±SEM) lung nodules are indicated by the horizontal bars. This experiment is representative of 2 completed independently. (B) Cytotoxicity of 4T1 tumor cells by activated WT vs. IL-10−/− 4T1 TDLN B cells as measured in an LDH release assay. Cytotoxicity was plotted against the ratio of effector B cells: tumor target cells (E:T ratio) which were plated in triplicate wells. Renca and TSA, both syngeneic to BALB/c mice, were used as specificity controls. Results are shown as mean ± SEM of triplicate wells from a single experiment representative of two experiments performed. *p<0.05, WT or IL-10−/− B cells + 4T1 vs. + Renca or + TSA; ▲p<0.05, IL-10−/− B cells + 4T1 vs. WT B cells + 4T1. P-values are indicated and were determined by Student’s t-test